B-cell receptor signaling as a driver of lymphoma development and evolution
- PMID: 24060900
- PMCID: PMC4208312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.09.001
B-cell receptor signaling as a driver of lymphoma development and evolution
Abstract
The B-cell receptor (BCR) is essential for normal B-cell development and maturation. In an increasing number of B-cell malignancies, BCR signaling is implicated as a pivotal pathway in tumorigenesis. Mechanisms of BCR activation are quite diverse and range from chronic antigenic drive by microbial or viral antigens to autostimulation of B-cells by self-antigens to activating mutations in intracellular components of the BCR pathway. Hepatitis C virus infection can lead to the development of splenic marginal zone lymphoma, while Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with the development of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. In some of these cases, successful treatment of the infection removes the inciting antigen and results in resolution of the lymphoma. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia has been recognized for decades as a malignancy of auto-reactive B-cells and its clinical course is in part determined by the differential response of the malignant cells to BCR activation. In a number of B-cell malignancies, activating mutations in signal transduction components of the BCR pathway have been identified; prominent examples are activated B-cell-like (ABC) diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) that carry mutations in CD79B and CARD11 and display chronic active BCR signaling resulting in constitutive activation of the NF-κB pathway. Despite considerable heterogeneity in biology and clinical course, many mature B-cell malignancies are highly sensitive to kinase inhibitors that disrupt BCR signaling. Thus, targeted therapy through inhibition of BCR signaling is emerging as a new treatment paradigm for many B-cell malignancies. Here, we review the role of the BCR in the pathogenesis of B-cell malignancies and summarize clinical results of the emerging class of kinase inhibitors that target this pathway.
Keywords: Antigen; B-cell receptor; Ibrutinib; Idelalisib; Lymphoma.
Copyright © 2013. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
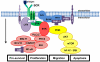

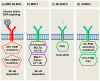
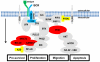
References
-
- Stevenson FK, Krysov S, Davies AJ, Steele AJ, Packham G. B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2011 Oct 20;118(16):4313–20. - PubMed
-
- Wiestner A. Targeting B-Cell receptor signaling for anticancer therapy: the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib induces impressive responses in B-cell malignancies. J.Clin.Oncol. 2013 Jan 1;31(1):128–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

