A novel noncanonical signaling pathway for the μ-opioid receptor
- PMID: 24061856
- PMCID: PMC3834144
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.113.088278
A novel noncanonical signaling pathway for the μ-opioid receptor
Abstract
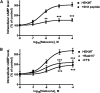
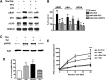
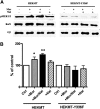
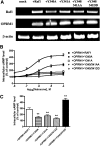
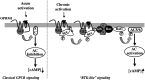
The µ-opioid receptor (OPRM1) signals as a classic G protein-coupled receptor by activating heterotrimeric Gi/Go proteins resulting in adenylyl cyclase (AC) inhibition. Such AC inhibition is desensitized after prolonged agonist treatment. However, after receptor desensitization, the intracellular cAMP level remains regulated by OPRM1, as demonstrated by the intracellular cAMP level increase or AC superactivation upon removal of an agonist or addition of an antagonist. We now demonstrate that such intracellular cAMP regulation is mediated by a novel noncanonical signaling pathway resulting from OPRM1 being converted to a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-like entity. This noncanonical OPRM1 signaling is initiated by the receptor recruiting and activating Src kinase within the receptor complex, leading to phosphorylation of the OPRM1 Tyr(336) residue. Phospho-Tyr(336) serves as the docking site for growth factor receptor-bound protein/son of sevenless, leading to the recruitment and activation of the Ras/Raf-1 and subsequent phosphorylation and activation of AC5/6 by Raf-1. Such sequence of events was established by the absence of Ras/Raf1 recruitment and activation by the OPRM1-Y336F mutant, by the presence of Src kinase inhibitor 4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine (PP2) or the absence of Src activity, by the presence of specific Raf-1 inhibitor GW5074 (5-iodo-3-[(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl) methylene]-2-indolinone) or the absence of Raf-1, or by the dominant negative RasN17 mutant. Src together with Ras activates Raf1 which was established by the inability of the Raf1-Tyr(340/341) mutant to activate AC. Hence, the phosphorylation of OPRM1 at Tyr(336) by Src serves as the trigger for the conversion of a classic Gi/Go-coupled receptor into an RTK-like entity, resulting in a noncanonical pathway even after the original Gi/Go signals are blunted.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Src phosphorylation of micro-receptor is responsible for the receptor switching from an inhibitory to a stimulatory signal.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 23;284(4):1990-2000. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807971200. Epub 2008 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19029294 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor-dependent increases in nitric oxide synthase expression in the pulmonary endothelium is mediated via a G alpha i3/Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):C2185-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00204.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17329403
-
Gi-mediated activation of the Ras/MAP kinase pathway involves a 100 kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated Grb2 SH3 binding protein, but not Src nor Shc.EMBO J. 1997 Jun 2;16(11):3097-105. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.11.3097. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9214627 Free PMC article.
-
Ras activation of the Raf kinase: tyrosine kinase recruitment of the MAP kinase cascade.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:127-55. doi: 10.1210/rp.56.1.127. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001. PMID: 11237210 Review.
-
Neuro2A differentiation by Galphai/o pathway.Sci Signal. 2009 Jan 20;2(54):cm1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.254cm1. Sci Signal. 2009. PMID: 19155528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of GPCR (mu-opioid)-receptor tyrosine kinase (epidermal growth factor) crosstalk in opioid-induced hyperalgesic priming (type II).Pain. 2018 May;159(5):864-875. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001155. Pain. 2018. PMID: 29447132 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Specific Regulation of P2X7 Receptor Function in Microglia Gates Morphine Analgesic Tolerance.J Neurosci. 2017 Oct 18;37(42):10154-10172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0852-17.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28924009 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular signalling of non-synonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the human μ-opioid receptor (OPRM1).Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):349-63. doi: 10.1111/bph.12644. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24527749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Signaling Profiles Reveal Unsuspected Functional Selectivity of δ-Opioid Receptor Agonists and Allow the Identification of Ligands with the Greatest Potential for Inducing Cyclase Superactivation.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021 Sep 9;4(5):1483-1498. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00019. eCollection 2021 Oct 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34661070 Free PMC article.
-
Depolarization-Dependent C-Raf Signaling Promotes Hyperexcitability and Reduces Opioid Sensitivity of Isolated Nociceptors after Spinal Cord Injury.J Neurosci. 2020 Aug 19;40(34):6522-6535. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0810-20.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 20. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32690613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avidor-Reiss T, Nevo I, Levy R, Pfeuffer T, Vogel Z. (1996) Chronic opioid treatment induces adenylyl cyclase V superactivation. Involvement of Gβγ. J Biol Chem 271:21309–21315 - PubMed
-
- Avidor-Reiss T, Nevo I, Saya D, Bayewitch M, Vogel Z. (1997) Opiate-induced adenylyl cyclase superactivation is isozyme-specific. J Biol Chem 272:5040–5047 - PubMed
-
- Baccarini M. (2005) Second nature: biological functions of the Raf-1 “kinase”. FEBS Lett 579:3271–3277 - PubMed
-
- Belcheva MM, Haas PD, Tan Y, Heaton VM, Coscia CJ. (2002) The fibroblast growth factor receptor is at the site of convergence between mu-opioid receptor and growth factor signaling pathways in rat C6 glioma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:909–918 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

