Identification of conformationally sensitive residues essential for inhibition of vesicular monoamine transport by the noncompetitive inhibitor tetrabenazine
- PMID: 24062308
- PMCID: PMC3820856
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.502971
Identification of conformationally sensitive residues essential for inhibition of vesicular monoamine transport by the noncompetitive inhibitor tetrabenazine
Abstract
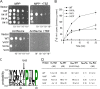
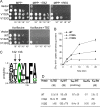
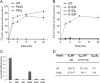
Vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) transports monoamines into storage vesicles in a process that involves exchange of the charged monoamine with two protons. VMAT2 is a member of the DHA12 family of multidrug transporters that belongs to the major facilitator superfamily of secondary transporters. Tetrabenazine (TBZ) is a non-competitive inhibitor of VMAT2 that is used in the treatment of hyperkinetic disorders associated with Huntington disease and Tourette syndrome. Previous biochemical studies suggested that the recognition site for TBZ and monoamines is different. However, the precise mechanism of TBZ interaction with VMAT2 remains unknown. Here we used a random mutagenesis approach and selected TBZ-resistant mutants. The mutations clustered around the lumenal opening of the transporter and mapped to either conserved proline or glycine, or to residues immediately adjacent to conserved proline and glycine. Directed mutagenesis provides further support for the essential role of the latter residues. Our data strongly suggest that the conserved α-helix breaking residues identified in this work play an important role in conformational rearrangements required for TBZ binding and substrate transport. Our results provide a novel insight into the mechanism of transport and TBZ binding by VMAT2.
Keywords: Directed Evolution; Ion-coupled Transporters; MFS Superfamily; Membrane Proteins; Multidrug Transporters; Neurotransmitter Transport; Neurotransmitters; PXXP Motifs.
Figures
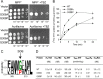
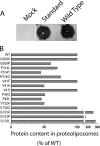
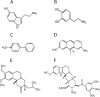
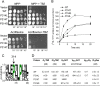

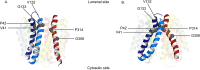
Similar articles
-
A fluorescent-based assay for live cell, spatially resolved assessment of vesicular monoamine transporter 2-mediated neurotransmitter transport.J Neurosci Methods. 2012 Aug 15;209(2):357-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Jun 12. J Neurosci Methods. 2012. PMID: 22698664 Free PMC article.
-
Emulating proton-induced conformational changes in the vesicular monoamine transporter VMAT2 by mutagenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):E7390-E7398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1605162113. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27821772 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrabenazine, a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 inhibitor, inhibits vesicular storage capacity and release of monoamine transmitters in mouse brain tissue.Br J Pharmacol. 2024 Dec;181(24):5094-5109. doi: 10.1111/bph.17348. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39304979
-
Comparing pharmacologic mechanism of action for the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors valbenazine and deutetrabenazine in treating tardive dyskinesia: does one have advantages over the other?CNS Spectr. 2018 Aug;23(4):239-247. doi: 10.1017/S1092852918001219. CNS Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30160230 Review.
-
Deutetrabenazine for the treatment of Huntington's chorea.Expert Rev Neurother. 2018 Aug;18(8):625-631. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2018.1500178. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018. PMID: 29996061 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of VMAT2 by β2-adrenergic agonists, antagonists, and the atypical antipsychotic ziprasidone.Commun Biol. 2022 Nov 23;5(1):1283. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04121-1. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36418492 Free PMC article.
-
Transport and inhibition mechanism for VMAT2-mediated synaptic vesicle loading of monoamines.Cell Res. 2024 Jan;34(1):47-57. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00906-z. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38163846 Free PMC article.
-
The ins and outs of vesicular monoamine transporters.J Gen Physiol. 2018 May 7;150(5):671-682. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201711980. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Gen Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29666153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of nitrate uptake by the plant nitrate transporter NRT1.1.Nature. 2014 Mar 6;507(7490):68-72. doi: 10.1038/nature13116. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24572366 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of neurotransmitter transport and drug inhibition in human VMAT2.Nature. 2023 Nov;623(7989):1086-1092. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06727-9. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37914936
References
-
- Schuldiner S., Shirvan A., Linial M. (1995) Vesicular neurotransmitter transporters. From bacteria to humans. Physiol. Rev. 75, 369–392 - PubMed
-
- Eiden L. E. (2000) The vesicular neurotransmitter transporters. Current perspectives and future prospects. FASEB J. 14, 2396–2400 - PubMed
-
- Parsons S. M. (2000) Transport mechanisms in acetylcholine and monoamine storage. FASEB J. 14, 2423–2434 - PubMed
-
- Erickson J. D., Varoqui H. (2000) Molecular analysis of vesicular amine transporter function and targeting to secretory organelles. FASEB J. 14, 2450–2458 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

