Unraveling the anxious mind: anxiety, worry, and frontal engagement in sustained attention versus off-task processing
- PMID: 24062316
- PMCID: PMC4318530
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bht248
Unraveling the anxious mind: anxiety, worry, and frontal engagement in sustained attention versus off-task processing
Abstract
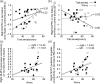
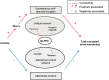
Much remains unknown regarding the relationship between anxiety, worry, sustained attention, and frontal function. Here, we addressed this using a sustained attention task adapted for functional magnetic resonance imaging. Participants responded to presentation of simple stimuli, withholding responses to an infrequent "No Go" stimulus. Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) activity to "Go" trials, and dorsal anterior cingulate (dACC) activity to "No Go" trials were associated with faster error-free performance; consistent with DLPFC and dACC facilitating proactive and reactive control, respectively. Trait anxiety was linked to reduced recruitment of these regions, slower error-free performance, and decreased frontal-thalamo-striatal connectivity. This indicates an association between trait anxiety and impoverished frontal control of attention, even when external distractors are absent. In task blocks where commission errors were made, greater DLPFC-precuneus and DLPFC-posterior cingulate connectivity were associated with both trait anxiety and worry, indicative of increased off-task thought. Notably, unlike trait anxiety, worry was not linked to reduced frontal-striatal-thalamo connectivity, impoverished frontal recruitment, or slowed responding during blocks without commission errors, contrary to accounts proposing a direct causal link between worry and impoverished attentional control. This leads us to propose a new model of the relationship between anxiety, worry and frontal engagement in attentional control versus off-task thought.
Keywords: anxiety; frontal function; off-task thought; sustained attention; worry.
© The Author 2013. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Worry is associated with inefficient functional activity and connectivity in prefrontal and cingulate cortices during emotional interference.Brain Behav. 2018 Dec;8(12):e01137. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1137. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 30378289 Free PMC article.
-
Using connectivity-based real-time fMRI neurofeedback to modulate attentional and resting state networks in people with high trait anxiety.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102191. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102191. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32044712 Free PMC article.
-
Trait anxiety modulates anterior cingulate activation to threat interference.Depress Anxiety. 2011 Mar;28(3):194-201. doi: 10.1002/da.20802. Depress Anxiety. 2011. PMID: 21394852 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of functional connectivity between anterior cingulate cortex and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on executive control of attention in healthy individuals].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Apr 2;93(13):995-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23886263 Chinese.
-
Proactive and reactive control during emotional interference and its relationship to trait anxiety.Brain Res. 2012 Oct 24;1481:13-36. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.08.045. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22960116 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gray-Matter Morphometry of Internalizing-Symptom Dimensions During Adolescence.Clin Psychol Sci. 2022 Sep;10(5):941-959. doi: 10.1177/21677026211071091. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Clin Psychol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36211328 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Theta-Burst Stimulation to the Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex May Increase Potentiated Startle in Healthy Individuals.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2022 Apr 25;3(3):470-479. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2022.04.001. eCollection 2023 Jul. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 37519467 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Brain Gray Matter Changes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 18;10(1):9925. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67022-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32555374 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Segregation Between Cognitive and Emotional Processes in Cannabis Dependence.Cereb Cortex. 2020 Mar 21;30(2):628-639. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhz113. Cereb Cortex. 2020. PMID: 31211388 Free PMC article.
-
Proactive control in adolescents and young adults with autism spectrum disorder: Unimpaired but associated with symptoms of depression.J Abnorm Psychol. 2020 Jul;129(5):517-527. doi: 10.1037/abn0000527. Epub 2020 May 14. J Abnorm Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32406696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beiser DG, Houk JC. Model of cortical-basal ganglionic processing: encoding the serial order of sensory events. J Neurophy. 1998;796:3168–3188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

