Effects of adding linagliptin to basal insulin regimen for inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a ≥52-week randomized, double-blind study
- PMID: 24062327
- PMCID: PMC3836100
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-2718
Effects of adding linagliptin to basal insulin regimen for inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a ≥52-week randomized, double-blind study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and long-term safety of linagliptin added to basal insulins in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin with or without oral agents.
Research design and methods: A total of 1,261 patients (HbA1c ≥7.0% [53 mmol/mol] to ≤10.0% [86 mmol/mol]) on basal insulin alone or combined with metformin and/or pioglitazone were randomized (1:1) to double-blind treatment with linagliptin 5 mg once daily or placebo for ≥52 weeks. The basal insulin dose was kept unchanged for 24 weeks but could thereafter be titrated according to fasting plasma glucose levels at the investigators' discretion. The primary end point was the mean change in HbA1c from baseline to week 24. The safety analysis incorporated data up to a maximum of 110 weeks.
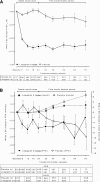
Results: At week 24, HbA1c changed from a baseline of 8.3% (67 mmol/mol) by -0.6% (-6.6 mmol/mol) and by 0.1% (1.1 mmol/mol) with linagliptin and placebo, respectively (treatment difference -0.65% [95% CI -0.74 to -0.55] [-7.1 mmol/mol]; P < 0.0001). Despite the option to uptitrate basal insulin, it was adjusted only slightly upward (week 52, linagliptin 2.6 IU/day, placebo 4.2 IU/day; P < 0.003), resulting in no further HbA1c improvements. Frequencies of hypoglycemia (week 24, linagliptin 22.0%, placebo 23.2%; treatment end, linagliptin 31.4%, placebo 32.9%) and adverse events (linagliptin 78.4%, placebo 81.4%) were similar between groups. Mean body weight remained unchanged (week 52, linagliptin -0.30 kg, placebo -0.04 kg).
Conclusions: Linagliptin added to basal insulin therapy significantly improved glycemic control relative to placebo without increasing hypoglycemia or body weight.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00954447.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenstock J, Sugimoto D, Strange P, Stewart JA, Soltes-Rak E, Dailey G. Triple therapy in type 2 diabetes: insulin glargine or rosiglitazone added to combination therapy of sulfonylurea plus metformin in insulin-naive patients. Diabetes Care 2006;29:554–559 - PubMed
-
- Hermansen K, Davies M, Derezinski T, Martinez Ravn G, Clauson P, Home P. A 26-week, randomized, parallel, treat-to-target trial comparing insulin detemir with NPH insulin as add-on therapy to oral glucose-lowering drugs in insulin-naive people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1269–1274 - PubMed
-
- Riddle MC, Rosenstock J, Gerich J, Insulin Glargine 4002 Study Investigators The treat-to-target trial: randomized addition of glargine or human NPH insulin to oral therapy of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3080–3086 - PubMed
-
- Yki-Järvinen H, Juurinen L, Alvarsson M, et al. Initiate Insulin by Aggressive Titration and Education (INITIATE): a randomized study to compare initiation of insulin combination therapy in type 2 diabetic patients individually and in groups. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1364–1369 - PubMed
-
- Drucker DJ, Nauck MA. The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2006;368:1696–1705 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical