Acutely increasing δGABA(A) receptor activity impairs memory and inhibits synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus
- PMID: 24062648
- PMCID: PMC3775149
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00146
Acutely increasing δGABA(A) receptor activity impairs memory and inhibits synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus
Abstract
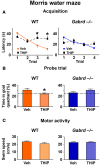
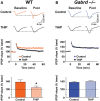
Extrasynaptic γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) receptors that contain the δ subunit (δGABA(A) receptors) are expressed in several brain regions including the dentate gyrus (DG) and CA1 subfields of the hippocampus. Drugs that increase δGABA(A) receptor activity have been proposed as treatments for a variety of disorders including insomnia, epilepsy and chronic pain. Also, long-term pretreatment with the δGABA(A) receptor-preferring agonist 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol (THIP) enhances discrimination memory and increases neurogenesis in the DG. Despite the potential therapeutic benefits of such treatments, the effects of acutely increasing δGABA(A) receptor activity on memory behaviors remain unknown. Here, we studied the effects of THIP (4 mg/kg, i.p.) on memory performance in wild-type (WT) and δGABA(A) receptor null mutant (Gabrd(-/-)) mice. Additionally, the effects of THIP on long-term potentiation (LTP), a molecular correlate of memory, were studied within the DG and CA1 subfields of the hippocampus using electrophysiological recordings of field potentials in hippocampal slices. The results showed that THIP impaired performance in the Morris water maze, contextual fear conditioning and object recognition tasks in WT mice but not Gabrd(-/-) mice. Furthermore, THIP inhibited LTP in hippocampal slices from WT but not Gabrd(-/-) mice, an effect that was blocked by GABA(A) receptor antagonist bicuculline. Thus, acutely increasing δGABA(A) receptor activity impairs memory behaviors and inhibits synaptic plasticity. These results have important implications for the development of therapies aimed at increasing δGABA(A) receptor activity.
Keywords: CA1; THIP; dentate gyrus; extrasynaptic GABAA receptors; long-term potentiation; memory; tonic inhibition; δ subunit.
Figures







Similar articles
-
γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors that contain the δ subunit promote memory and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus.Ann Neurol. 2013 Oct;74(4):611-21. doi: 10.1002/ana.23941. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Ann Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23686887
-
Pharmacological enhancement of δ-subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors that generate a tonic inhibitory conductance in spinal neurons attenuates acute nociception in mice.Pain. 2011 Jun;152(6):1317-1326. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.02.011. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Pain. 2011. PMID: 21396779
-
δGABAA Receptors Are Necessary for Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus: Implications for Memory Behavior.Anesth Analg. 2016 Nov;123(5):1247-1252. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001373. Anesth Analg. 2016. PMID: 27464975
-
GABA-A Receptors Mediate Tonic Inhibition and Neurosteroid Sensitivity in the Brain.Vitam Horm. 2018;107:177-191. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2017.12.001. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Vitam Horm. 2018. PMID: 29544630 Review.
-
Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors are critical targets for sedative-hypnotic drugs.J Clin Sleep Med. 2006 Apr 15;2(2):S12-8. J Clin Sleep Med. 2006. PMID: 17557502 Review.
Cited by
-
Bidirectional plasticity of GABAergic tonic inhibition in hippocampal somatostatin- and parvalbumin-containing interneurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jun 28;17:1193383. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1193383. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37448697 Free PMC article.
-
An Emerging Circuit Pharmacology of GABAA Receptors.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Aug;39(8):710-732. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29903580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Yin and Yang of GABAergic and Glutamatergic Synaptic Plasticity: Opposites in Balance by Crosstalking Mechanisms.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022 May 19;14:911020. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2022.911020. eCollection 2022. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35663370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal Transcriptome Profile of Persistent Memory Rescue in a Mouse Model of THRA1 Mutation-Mediated Resistance to Thyroid Hormone.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 8;6:18617. doi: 10.1038/srep18617. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26743578 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of GABAa receptor antagonists on motor behavior in pharmacological Parkinson's disease model in mice.Physiol Rep. 2017 Mar;5(6):e13081. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13081. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28351968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai D., Zhu G., Pennefather P., Jackson M. F., MacDonald J. F., Orser B. A. (2001). Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of tonic and quantal inhibitory postsynaptic currents mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors in hippocampal neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 814–824 - PubMed
-
- Bonin R. P., Labrakakis C., Eng D. G., Whissell P. D., Koninck Y. D., Orser B. A. (2011). Pharmacological enhancement of δ-subunit-containing GABAA receptors that generate a tonic inhibitory conductance in spinal neurons attenuates acute nociception in mice. Pain 152, 1317–1326 10.1016/j.pain.2011.02.011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

