Oxidative stress is involved in the pathogenesis of Keshan disease (an endemic dilated cardiomyopathy) in China
- PMID: 24062877
- PMCID: PMC3770050
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/474203
Oxidative stress is involved in the pathogenesis of Keshan disease (an endemic dilated cardiomyopathy) in China
Abstract
Oxidative stress and selenoprotein deficiency are thought to be associated with the pathogenesis of Keshan disease (KD). However, to our knowledge, the level of oxidative stress and expression of selenoproteins have not been investigated in the myocardium of patients with KD. In this study, 8-hydroxy-2-deoxy guanosine (8-OH-dG), a marker of oxidative stress, was used to assess the level of oxidative stress, and thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) and glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1) were assessed to reflect the level of selenoproteins. Myocardial samples from 8 patients with KD and 9 non-KD patients (controls) were immunohistochemically stained for 8-OH-dG, TrxR1, and GPx1. The staining intensities were subsequently quantified using Olympus Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software. The data showed that the positive rate of 8-OH-dG expression in myocardial nuclei was higher in the KD group (68.6%) than that in the control group (2.4%). In addition, a positive correlation between the positive rate of 8-OH-dG and the degree of myocardial damage was observed in the KD group. The distribution of TrxR1 and GPx-1 was not associated with the distribution of myocardial damage. The expression of these two selenoproteins was higher in the control group than that in the KD group. Our study represents the first report on the expression profiles of oxidative stress and selenoproteins in the myocardium of patients with KD. The level of oxidative stress significantly increased and was positively correlated with the degree of myocardial damage in patients with KD. The selenoproteins, TrxR1 and GPx1, may have a role in the pathogenesis of KD.
Figures

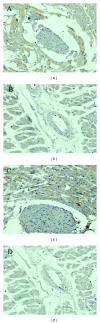
References
-
- Lei C, Niu X, Ma X, Wei J. Is selenium deficiency really the cause of Keshan Disease? Environmental Geochemistry and Health. 2011;33(2):183–188. - PubMed
-
- Keshan Disease Research Group. Observations on effect of sodium selenite in prevention of Keshan Disease. Chinese Medical Journal. 1979;92:471–476. - PubMed
-
- Jia C, Chen X, Li X, et al. The effect of DHEA treatment on the oxidative stress and myocardial fibrosis induced by Keshan Disease pathogenic factors. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology. 2011;25(3):154–159. - PubMed
-
- Battin EE, Brumaghim JL. Antioxidant activity of sulfur and selenium: a review of reactive oxygen species scavenging, glutathione peroxidase, and metal-binding antioxidant mechanisms. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2009;55(1):1–23. - PubMed
-
- Khalil WKB, Girgis E, Emam AN, Mohamed MB, Rao KV. Genotoxicity evaluation of nanomaterials: DNA damage, micronuclei, and 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine induced by magnetic doped CdSe quantum dots in male mice. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 2011;24(5):640–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

