Impaired binding of standard initiation factors eIF3b, eIF4G and eIF4B to domain V of the live-attenuated coxsackievirus B3 Sabin3-like IRES--alternatives for 5'UTR-related cardiovirulence mechanisms
- PMID: 24063684
- PMCID: PMC3853319
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-161
Impaired binding of standard initiation factors eIF3b, eIF4G and eIF4B to domain V of the live-attenuated coxsackievirus B3 Sabin3-like IRES--alternatives for 5'UTR-related cardiovirulence mechanisms
Abstract
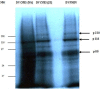
Internal ribosome entry site (IRES) elements fold into highly organized conserved secondary and probably tertiary structures that guide the ribosome to an internal site of the RNA at the IRES 3'end. The composition of the cellular proteome is under the control of multiple processes, one of the most important being translation initiation. In each poliovirus Sabin vaccine strain, a single point mutation in the IRES secondary-structure domain V is a major determinant of neurovirulence and translation attenuation. Here we are extrapolating poliovirus findings to a genomic related virus named coxsackievirus B3 CVB3); a causative agent of viral myocarditis. We have previously reported that Sabin3-like mutation (U473 → C) introduced in the domain V sequence of the CVB3 IRES led to a defective mutant with a serious reduction in translation efficiency and ribosomal initiation complex assembly, besides an impaired RNA-protein binding pattern. With the aim to identify proteins interacting with both CVB3 wild-type and Sabin3-like domain V RNAs and to assess the effect of the Sabin3-like mutation on these potential interactions, we have used a proteomic approach. This procedure allowed the identification of three RNA-binding proteins interacting with the domain V: eIF4G (p220), eIF3b (p116) and eIF4B (p80). Moreover, we report that this single-nucleotide exchange impairs the interaction pattern and the binding affinity of these standard translation initiation factors within the IRES domain V of the mutant strain. Taken together, these data indicate how this decisive Sabin3-like mutation mediates viral translation attenuation; playing a key role in the understanding of the cardiovirulence attenuation within this construct. Hence, these data provide further evidence for the crucial role of RNA structure for the IRES activity, and reinforce the idea of a distribution of function between the different IRES structural domains.
Virtual slide: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/6160165131045880.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vitro molecular characterization of RNA-proteins interactions during initiation of translation of a wild-type and a mutant Coxsackievirus B3 RNAs.Mol Biotechnol. 2013 Jun;54(2):515-27. doi: 10.1007/s12033-012-9592-x. Mol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22923320
-
In vitro-reduced translation efficiency of coxsackievirus B3 Sabin3-like strain is correlated to impaired binding of cellular initiation factors to viral IRES RNA.Curr Microbiol. 2015 May;70(5):756-61. doi: 10.1007/s00284-015-0784-z. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Curr Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25673016
-
The substitution U475 --> C with Sabin3-like mutation within the IRES attenuate Coxsackievirus B3 cardiovirulence.Mol Biotechnol. 2007 May;36(1):52-60. doi: 10.1007/s12033-007-0019-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17827538
-
Role of RNA structure motifs in IRES-dependent translation initiation of the coxsackievirus B3: new insights for developing live-attenuated strains for vaccines and gene therapy.Mol Biotechnol. 2013 Oct;55(2):179-202. doi: 10.1007/s12033-013-9674-4. Mol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23881360 Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Translation Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 27;21(7):2328. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072328. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32230899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Incompatible Translation Drives a Convergent Evolution and Viral Attenuation During the Development of Live Attenuated Vaccine.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jul 18;8:249. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00249. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30073153 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the common genetic landscape of COVID-19 and male infertility.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 20;14:1123913. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123913. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37020555 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on circular RNA vaccines.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 12;13:1091797. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1091797. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36713460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening and analysis on the protein interaction of the protein VP7 in grass carp reovirus.Virus Genes. 2015 Jun;50(3):425-33. doi: 10.1007/s11262-015-1193-x. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Virus Genes. 2015. PMID: 25860999
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

