Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin provides neuroprotection after experimental stroke in aged rats
- PMID: 24063996
- PMCID: PMC3877728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.09.008
Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin provides neuroprotection after experimental stroke in aged rats
Abstract
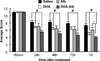
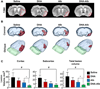
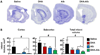
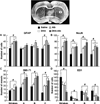
Recently we have shown that docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin (DHA-Alb) is neuroprotective after experimental stroke in young rats. The purpose of this study was to determine whether treatment with DHA-Alb would be protective in aged rats after focal cerebral ischemia. Isoflurane/nitrous oxide-anesthetized normothermic (brain temperature 36-36.5°C) Sprague-Dawley aged rats (18-months old) received 2h middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) by poly-l-lysine-coated intraluminal suture. The neurological status was evaluated during occlusion (60min) and on days 1, 2, 3 and 7 after MCAo; a grading scale of 0-12 was employed. DHA (5mg/kg), Alb (0.63g/kg), DHA-Alb (5mg/kg+0.63g/kg) or saline was administered i.v. 3h after onset of stroke (n=8-10 per group). Ex vivo T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) of the brains was conducted on an 11.7T MRI on day 7 and 3D reconstructions were generated. Infarct volumes and number of GFAP (reactive astrocytes), ED-1 (activated microglia/microphages), NeuN (neurons)-positive cells and SMI-71 (positive vessels) were counted in the cortex and striatum at the level of the central lesion. Physiological variables were entirely comparable between groups. Animals treated with DHA-Alb showed significantly improved neurological scores compared to vehicle rats; 33% improvement on day 1; 39% on day 2; 41% on day 3; and 45% on day 7. Total and cortical lesion volumes computed from T2WI were significantly reduced by DHA-Alb treatment (62 and 69%, respectively). In addition, treatment with DHA-Alb reduced cortical and total brain infarction while promoting cell survival. We conclude that DHA-Alb therapy is highly neuroprotective in aged rats following focal cerebral ischemia and has potential for the effective treatment of ischemic stroke in aged individuals.
Keywords: Behavior; Histopathology; Magnetic resonance imaging; Middle cerebral artery occlusion; Rat; Stroke.
© 2013. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute treatment with docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin reduces injury after a permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 23;8(10):e77237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077237. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24194876 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to human albumin in experimental stroke: neuroprotective efficacy with a wide therapeutic window.Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2012 Sep 14;4(1):19. doi: 10.1186/2040-7378-4-19. Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2012. PMID: 22980673 Free PMC article.
-
Novel aspirin-triggered neuroprotectin D1 attenuates cerebral ischemic injury after experimental stroke.Exp Neurol. 2012 Jul;236(1):122-30. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.04.007. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22542947 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin and lipid enriched albumin for the critically ill.J Assoc Physicians India. 2009 Jan;57:53-9. J Assoc Physicians India. 2009. PMID: 19753760 Review.
-
Developing a standardized system of exposure and intervention endpoints for isoflurane in preclinical stroke models.Med Gas Res. 2019 Jan-Mar;9(1):46-51. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.254640. Med Gas Res. 2019. PMID: 30950418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular profile of the rat peri-infarct region four days after stroke: Study with MANF.Exp Neurol. 2020 Jul;329:113288. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113288. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32229226 Free PMC article.
-
Marine-derived n-3 fatty acids therapy for stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 29;6(6):CD012815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012815.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35766825 Free PMC article.
-
Unsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Immunomodulatory Properties.Biology (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;12(2):279. doi: 10.3390/biology12020279. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone Marrow Stromal Cells With Exercise and Thyroid Hormone Effect on Post-Stroke Injuries in Middle-aged Mice.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2019 Jan-Feb;10(1):73-84. doi: 10.32598/bcn.9.10.355. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31031895 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Central Post-Stroke Pain: A Review.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;43(7):3083-3098. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01360-6. Epub 2023 May 11. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37166685 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bazan NG. Omega-3 fatty acids, pro-inflammatory signaling and neuroprotection. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2007;10:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Bazan NG. Cell survival matters: docosahexaenoic acid signaling, neuroprotection and photoreceptors. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:263–271. - PubMed
-
- Bazan NG. Synaptic lipid signaling: significance of polyunsaturated fatty acids and platelet-activating factor. J. Lipid Res. 2003;44:2221–2233. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Alonso OF, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by intraluminal suture. Neurological and pathological evaluation of an improved model. Stroke. 1996;27:1616–1622. discussion 1623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

