Use of magnetic resonance elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in children with chronic liver disease
- PMID: 24064151
- PMCID: PMC3872246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.07.050
Use of magnetic resonance elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in children with chronic liver disease
Abstract
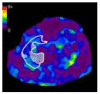
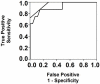
Management of pediatric chronic liver disease is limited by lack of validated noninvasive biomarkers of histologic severity. We demonstrate that magnetic resonance elastography is feasible and accurate in detecting significant hepatic fibrosis in a case series of 35 children with chronic liver disease, including severely obese children.
Keywords: ARFI; AUROC; Acoustic radiation force imaging; Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; BMI; Body mass index; MRE; Magnetic resonance elastography; NAFLD; NASH; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; ROI; Region of interest; TE; Transient elastography; US; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2014 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, Salameh N, Annet L, Danse E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:32–40. - PubMed
-
- Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–1321. - PubMed
-
- Serai SD, Towbin AJ, Podberesky DJ. Pediatric Liver MR Elastography. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:2713–2719. - PubMed
-
- Nobili V, Vizzutti F, Arena U, Abraldes JG, Marra F, Pietrobattista A, et al. Accuracy and reproducibility of transient elastography for the diagnosis of fibrosis in pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2008;48:442–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

