Defective prolactin signaling impairs pancreatic β-cell development during the perinatal period
- PMID: 24064341
- PMCID: PMC3840213
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00636.2012
Defective prolactin signaling impairs pancreatic β-cell development during the perinatal period
Abstract
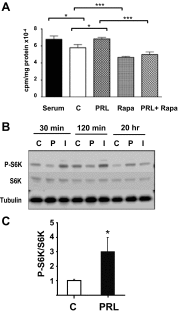
Prolactin (PRL) and placental lactogens stimulate β-cell replication and insulin production in pancreatic islets and insulinoma cells through binding to the PRL receptor (PRLR). However, the contribution of PRLR signaling to β-cell ontogeny and function in perinatal life and the effects of the lactogens on adaptive islet growth are poorly understood. We provide evidence that expansion of β-cell mass during both embryogenesis and the postnatal period is impaired in the PRLR(-/-) mouse model. PRLR(-/-) newborns display a 30% reduction of β-cell mass, consistent with reduced proliferation index at E18.5. PRL stimulates leucine incorporation and S6 kinase phosphorylation in INS-1 cells, supporting a role for β-cell mTOR signaling in PRL action. Interestingly, a defect in the development of acini is also observed in absence of PRLR signaling, with a sharp decline in cellular size in both endocrine and exocrine compartments. Of note, a decrease in levels of IGF-II, a PRL target, in the Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rat, a spontaneous model of type 2 diabetes, is associated with a lack of PRL-mediated β-cell proliferation in embryonic pancreatic buds. Reduced pancreatic IGF-II expression in both rat and mouse models suggests that this factor may constitute a molecular link between PRL signaling and cell ontogenesis. Together, these results provide evidence that PRL signaling is essential for pancreas ontogenesis during the critical perinatal window responsible for establishing functional β-cell reserve.
Keywords: IGF-II; apoptosis; diabetes; insulin; placental lactogens; proliferation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prolactin receptor signaling is essential for perinatal brown adipocyte function: a role for insulin-like growth factor-2.PLoS One. 2008 Feb 6;3(2):e1535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001535. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18253483 Free PMC article.
-
Diphenylbutylpiperidine Antipsychotic Drugs Inhibit Prolactin Receptor Signaling to Reduce Growth of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2020 Apr;158(5):1433-1449.e27. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.279. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 31786131 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogenesis of prolactin receptors in the human fetus: roles in fetal development.Biochem Soc Trans. 2001 May;29(Pt 2):38-41. doi: 10.1042/0300-5127:0290038. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. PMID: 11356123 Review.
-
Augmented Stat5 Signaling Bypasses Multiple Impediments to Lactogen-Mediated Proliferation in Human β-Cells.Diabetes. 2015 Nov;64(11):3784-97. doi: 10.2337/db15-0083. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26159175 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin receptor signaling: A novel target for cancer treatment - Exploring anti-PRLR signaling strategies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 13;13:1112987. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1112987. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36714582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 26;19(11):3342. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113342. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30373146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Role of 17-Beta Estradiol in the Regulation of the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) in Pancreatic Beta Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 2;25(3):1816. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031816. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339098 Free PMC article.
-
Cell biology. On being the right (cell) size.Science. 2015 May 15;348(6236):1245075. doi: 10.1126/science.1245075. Science. 2015. PMID: 25977557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The beneficial metabolic actions of prolactin.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 23;13:1001703. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1001703. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36213259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights in prolactin: pathological implications.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 May;11(5):265-75. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.36. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25781857 Review.
References
-
- Al Masri M, Krishnamurthy M, Li J, Fellows GF, Dong HH, Goodyer CG, Wang R. Effect of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) on β-cell development in the human fetal pancreas. Diabetologia 53: 699–711, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Arumugam R, Horowitz E, Lu D, Collier JJ, Ronnebaum S, Fleenor D, Freemark M. The interplay of prolactin and the glucocorticoids in the regulation of beta-cell gene expression, fatty acid oxidation, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: implications for carbohydrate metabolism in pregnancy. Endocrinology 149: 5401–5414, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binart N, Bachelot A, Bouilly J. Impact of prolactin receptor isoforms on reproduction. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21: 362–368, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

