Defective prolactin signaling impairs pancreatic β-cell development during the perinatal period
- PMID: 24064341
- PMCID: PMC3840213
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00636.2012
Defective prolactin signaling impairs pancreatic β-cell development during the perinatal period
Abstract
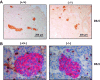
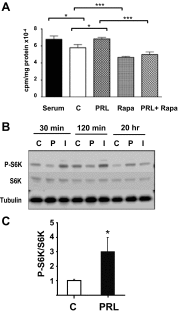
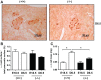
Prolactin (PRL) and placental lactogens stimulate β-cell replication and insulin production in pancreatic islets and insulinoma cells through binding to the PRL receptor (PRLR). However, the contribution of PRLR signaling to β-cell ontogeny and function in perinatal life and the effects of the lactogens on adaptive islet growth are poorly understood. We provide evidence that expansion of β-cell mass during both embryogenesis and the postnatal period is impaired in the PRLR(-/-) mouse model. PRLR(-/-) newborns display a 30% reduction of β-cell mass, consistent with reduced proliferation index at E18.5. PRL stimulates leucine incorporation and S6 kinase phosphorylation in INS-1 cells, supporting a role for β-cell mTOR signaling in PRL action. Interestingly, a defect in the development of acini is also observed in absence of PRLR signaling, with a sharp decline in cellular size in both endocrine and exocrine compartments. Of note, a decrease in levels of IGF-II, a PRL target, in the Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rat, a spontaneous model of type 2 diabetes, is associated with a lack of PRL-mediated β-cell proliferation in embryonic pancreatic buds. Reduced pancreatic IGF-II expression in both rat and mouse models suggests that this factor may constitute a molecular link between PRL signaling and cell ontogenesis. Together, these results provide evidence that PRL signaling is essential for pancreas ontogenesis during the critical perinatal window responsible for establishing functional β-cell reserve.
Keywords: IGF-II; apoptosis; diabetes; insulin; placental lactogens; proliferation.
Figures





References
-
- Al Masri M, Krishnamurthy M, Li J, Fellows GF, Dong HH, Goodyer CG, Wang R. Effect of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) on β-cell development in the human fetal pancreas. Diabetologia 53: 699–711, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Arumugam R, Horowitz E, Lu D, Collier JJ, Ronnebaum S, Fleenor D, Freemark M. The interplay of prolactin and the glucocorticoids in the regulation of beta-cell gene expression, fatty acid oxidation, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: implications for carbohydrate metabolism in pregnancy. Endocrinology 149: 5401–5414, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binart N, Bachelot A, Bouilly J. Impact of prolactin receptor isoforms on reproduction. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21: 362–368, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

