Amyloid-β oligomers induce synaptic damage via Tau-dependent microtubule severing by TTLL6 and spastin
- PMID: 24065130
- PMCID: PMC3831312
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.207
Amyloid-β oligomers induce synaptic damage via Tau-dependent microtubule severing by TTLL6 and spastin
Abstract
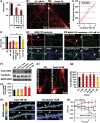
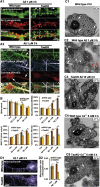
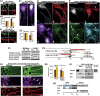
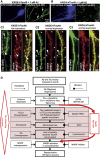
Mislocalization and aggregation of Aβ and Tau combined with loss of synapses and microtubules (MTs) are hallmarks of Alzheimer disease. We exposed mature primary neurons to Aβ oligomers and analysed changes in the Tau/MT system. MT breakdown occurs in dendrites invaded by Tau (Tau missorting) and is mediated by spastin, an MT-severing enzyme. Spastin is recruited by MT polyglutamylation, induced by Tau missorting triggered translocalization of TTLL6 (Tubulin-Tyrosine-Ligase-Like-6) into dendrites. Consequences are spine loss and mitochondria and neurofilament mislocalization. Missorted Tau is not axonally derived, as shown by axonal retention of photoconvertible Dendra2-Tau, but newly synthesized. Recovery from Aβ insult occurs after Aβ oligomers lose their toxicity and requires the kinase MARK (Microtubule-Affinity-Regulating-Kinase). In neurons derived from Tau-knockout mice, MTs and synapses are resistant to Aβ toxicity because TTLL6 mislocalization and MT polyglutamylation are prevented; hence no spastin recruitment and no MT breakdown occur, enabling faster recovery. Reintroduction of Tau re-establishes Aβ-induced toxicity in TauKO neurons, which requires phosphorylation of Tau's KXGS motifs. Transgenic mice overexpressing Tau show TTLL6 translocalization into dendrites and decreased MT stability. The results provide a rationale for MT stabilization as a therapeutic approach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
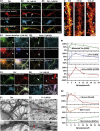
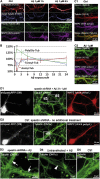
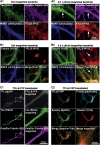
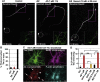
Comment in
-
It cuts two ways: microtubule loss during Alzheimer disease.EMBO J. 2013 Nov 13;32(22):2900-2. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.219. Epub 2013 Sep 27. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 24076651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustinack JC, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Hyman BT (2002) Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropath 103: 26–35 - PubMed
-
- Baas PW, Karabay A, Qiang L (2005) Microtubules cut and run. Trends Cell Biol 15: 518–524 - PubMed
-
- Bano D, Nicotera P (2007) Ca2+ signals and neuronal death in brain ischemia. Stroke 38: 674–676 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

