Transgenic muscle-specific Nor-1 expression regulates multiple pathways that effect adiposity, metabolism, and endurance
- PMID: 24065705
- PMCID: PMC5427836
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2013-1205
Transgenic muscle-specific Nor-1 expression regulates multiple pathways that effect adiposity, metabolism, and endurance
Abstract
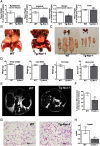
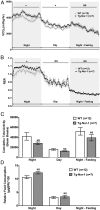
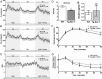
The mRNA encoding Nor-1/NR4A3 is rapidly and strikingly induced by β2-adrenergic signaling in glycolytic and oxidative skeletal muscle. In skeletal muscle cells, Nor-1 expression is important for the regulation of oxidative metabolism. Transgenic skeletal muscle-specific expression of activated Nor-1 resulted in the acquisition of an endurance phenotype, an increase in type IIA/X oxidative muscle fibers, and increased numbers of mitochondria. In the current study, we used dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and magnetic resonance imaging analysis to demonstrate decreased adiposity in transgenic (Tg) Nor-1 mice relative to that in wild-type littermates. Furthermore, the Tg-Nor-1 mice were resistant to diet-induced weight gain and maintained fasting glucose at normoglycemic levels. Expression profiling and RT-quantitative PCR analysis revealed significant increases in genes involved in glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, fatty acid oxidation, and glycogen synthesis, in concordance with the lean phenotype. Moreover, expression profiling identified several Z-disc and sarcomeric binding proteins that modulate fiber type phenotype and endurance, eg, α-actinin-3. In addition, we demonstrated that the Tg-Nor-1 mouse line has significantly higher glycogen content in skeletal muscle relative to that in wild-type littermates. Finally, we identified a decreased NAD(+)/NADH ratio with a concordant increase in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α1 protein/mRNA expression. Increased NADH was associated with an induction of the genes involved in the malate-aspartate shuttle and a decrease in the glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle, which maximizes aerobic ATP production. In conclusion, skeletal muscle-specific Nor-1 expression regulates genes and pathways that regulate adiposity, muscle fiber type metabolic capacity, and endurance.
Figures




References
-
- Owen OE, Reichard GA Jr, Boden G, Patel MS, Trapp VE. Interrelationships among key tissues in the utilization of metabolic substrate. In Katzen HE, Mahler RJ, eds. Advances in Modern Nutrition. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons; 1978:517–550.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

