The basal forebrain modulates spontaneous activity of principal cells in the main olfactory bulb of anesthetized mice
- PMID: 24065892
- PMCID: PMC3778317
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00148
The basal forebrain modulates spontaneous activity of principal cells in the main olfactory bulb of anesthetized mice
Abstract
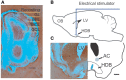
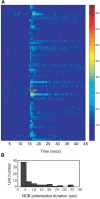
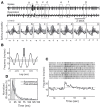
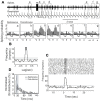
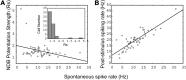
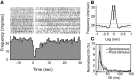
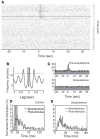
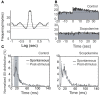
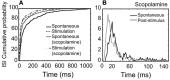
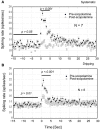
Spontaneous activity is an important characteristic of the principal cells in the main olfactory bulb (MOB) for encoding odor information, which is modulated by the basal forebrain. Cholinergic activation has been reported to inhibit all major neuron types in the MOB. In this study, the effect of diagonal band (NDB) stimulation on mitral/tufted (M/T) cell spontaneous activity was examined in anesthetized mice. NDB stimulation increased spontaneous activity in 66 MOB neurons which lasted for 2-35 s before returning to the baseline level. The majority of the effected units showed a decrease of interspike intervals (ISI) at a range of 8-25 ms. Fifty-two percent of NDB stimulation responsive units showed intrinsic rhythmical bursting, which was enhanced temporarily by NDB stimulation, whereas the remaining non-rhythmic units were capable of synchronized bursting. The effect was attenuated by scopolamine in 21 of 27 units tested. Only four NDB units were inhibited by NDB stimulation, an inhibition that lasted less than 10 s. The NDB stimulation responsive neurons appeared to be M/T cells. Our findings demonstrate an NDB excitation effect on M/T neurons that mostly requires muscarinic receptor activation, and is likely due to non-selectivity of electrical stimulation. This suggests that cholinergic and a diverse group of non-cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain co-ordinately modulate the dynamics of M/T cell spontaneous activity, which is fundamental for odor representation and attentional perception.
Keywords: diagonal band; mitral cell; olfactory bulb; scopolamine; synchronization; tufted cell.
Figures
References
-
- Buonviso N., Chaput M. A., Berthommier F. (1992). Temporal pattern analyses in pairs of neighboring mitral cells. J. Neurophysiol. 68, 417–424 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

