Blood pressure changes after renal denervation at 10 European expert centers
- PMID: 24067345
- PMCID: PMC3932403
- DOI: 10.1038/jhh.2013.88
Blood pressure changes after renal denervation at 10 European expert centers
Abstract
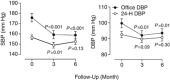
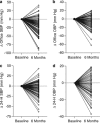
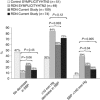
We did a subject-level meta-analysis of the changes (Δ) in blood pressure (BP) observed 3 and 6 months after renal denervation (RDN) at 10 European centers. Recruited patients (n=109; 46.8% women; mean age 58.2 years) had essential hypertension confirmed by ambulatory BP. From baseline to 6 months, treatment score declined slightly from 4.7 to 4.4 drugs per day. Systolic/diastolic BP fell by 17.6/7.1 mm Hg for office BP, and by 5.9/3.5, 6.2/3.4, and 4.4/2.5 mm Hg for 24-h, daytime and nighttime BP (P0.03 for all). In 47 patients with 3- and 6-month ambulatory measurements, systolic BP did not change between these two time points (P0.08). Normalization was a systolic BP of <140 mm Hg on office measurement or <130 mm Hg on 24-h monitoring and improvement was a fall of 10 mm Hg, irrespective of measurement technique. For office BP, at 6 months, normalization, improvement or no decrease occurred in 22.9, 59.6 and 22.9% of patients, respectively; for 24-h BP, these proportions were 14.7, 31.2 and 34.9%, respectively. Higher baseline BP predicted greater BP fall at follow-up; higher baseline serum creatinine was associated with lower probability of improvement of 24-h BP (odds ratio for 20-μmol l(-1) increase, 0.60; P=0.05) and higher probability of experiencing no BP decrease (OR, 1.66; P=0.01). In conclusion, BP responses to RDN include regression-to-the-mean and remain to be consolidated in randomized trials based on ambulatory BP monitoring. For now, RDN should remain the last resort in patients in whom all other ways to control BP failed, and it must be cautiously used in patients with renal impairment.
Figures
Comment in
-
Meta-methodology: conducting and reporting meta-analyses.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2014 Feb;16(2):91-3. doi: 10.1111/jch.12215. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2014. PMID: 24734310 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Renal denervation in moderate treatment-resistant hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Nov 12;62(20):1880-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.06.023. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23850901 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Alcohol-Mediated Renal Denervation on Blood Pressure in the Presence of Antihypertensive Medications: Primary Results From the TARGET BP I Randomized Clinical Trial.Circulation. 2024 Jun 11;149(24):1875-1884. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.069291. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Circulation. 2024. PMID: 38587557 Clinical Trial.
-
Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension after witnessed intake of medication before qualifying ambulatory blood pressure.Hypertension. 2013 Sep;62(3):526-32. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.01452. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23836798
-
What are the ideal metrics for assessing the quality of long-term stabilized "perfect" 24-h BP control after renal denervation?Hypertens Res. 2024 Oct;47(10):2644-2651. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01859-5. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 39191961 Review.
-
Effects of renal denervation on blood pressure in patients with hypertension: a latest systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized sham-controlled trials.Hypertens Res. 2024 Oct;47(10):2745-2759. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01739-y. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38831091
Cited by
-
Late outcomes of renal denervation are more favourable than early ones: facts or fancies?Clin Kidney J. 2023 Sep 20;16(12):2357-2364. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad231. eCollection 2023 Dec. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38046011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guideline of the Brazilian Society of Cardiology and the Brazilian College of Radiology - 2024.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024 Oct 28;121(9):e20240608. doi: 10.36660/abc.20240608. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39475988 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
-
Renal denervation therapy for resistant hypertension.Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2014 Dec;16(12):350. doi: 10.1007/s11936-014-0350-1. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2014. PMID: 25300359
-
Renal denervation in the treatment of resistant arterial hypertension.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014 Dec;164(23-24):515-8. doi: 10.1007/s10354-014-0330-9. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 25394989
-
Renal denervation after Symplicity HTN-3: an update.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014 Aug;16(8):460. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0460-x. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014. PMID: 24913923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Staessen JA, Kuznetsova T, Stolarz K. Hypertension prevalence and stroke mortality across populations. JAMA. 2003;289:2420–2422. - PubMed
-
- Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R, Sobotka PA, Sadowski J, Bartus K, et al. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet. 2009;373:1275–1281. - PubMed
-
- Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, Böhm M, Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:1903–1909. - PubMed
-
- Symplicity HTN-1 Investigators. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension. Durability of blood pressure reduction out to 24 months. Hypertension. 2011;57:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Azizi M, Steichen O, Frank M, Bobrie G, Plouin PF, Sapoval M. Catheter-based radiofrequency renal ablation in patients with resistant hypertension. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2012;43:293–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

