Complex effects of vitamin E and vitamin C supplementation on in vitro neonatal mononuclear cell responses to allergens
- PMID: 24067384
- PMCID: PMC3798907
- DOI: 10.3390/nu5093337
Complex effects of vitamin E and vitamin C supplementation on in vitro neonatal mononuclear cell responses to allergens
Abstract
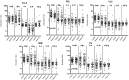
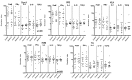
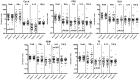
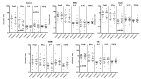
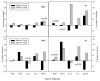
Low maternal dietary vitamin E (but not vitamin C) intake during pregnancy has been associated with increased in vitro cord blood mononuclear cell (CBMC) proliferative responses, childhood wheezing and asthma. We investigated whether these associations reflect direct effects of vitamin E by investigating the effects of supplementing CBMC cultures with physiological concentrations of vitamin E. CBMC from seventy neonates were cultured supplemented with either nothing, α-tocopherol or ascorbic acid. Proliferative, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-10 and TGF-β responses were measured. In general, vitamin E supplementation was associated with a trend for reduced proliferative responses after stimulation with antigens and house dust mite, and with increased proliferation after stimulation with timothy grass allergen. There was a trend for CBMC cultures to exhibit decreased secretion of IFN-γ, IL-10 and IL-4. Supplementation with vitamin C had no effect on CBMC proliferation, but increased IFN-γ and IL-4 production, and decreased IL-10 production. In conclusion, in vitro vitamin E and C supplementation of CBMC modifies neonatal immune function, but not in a manner predicted by observational epidemiological studies. The observed associations between vitamin E and childhood respiratory disease are complex, and the nature and form of nutritional intervention need to be carefully considered before inclusion in trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measurement of T-helper cytokines secreted by cord blood mononuclear cells in response to allergens.J Immunol Methods. 2000 Feb 3;234(1-2):13-22. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(99)00185-4. J Immunol Methods. 2000. PMID: 10669765
-
Correlation of Th1-type cytokine expression and induced proliferation to lipopolysaccharide.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Jun;38(6):733-7. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0143OC. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18218996
-
Interleukin-18 enhances the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) by allergen-specific and unspecific stimulated cord blood mononuclear cells.Cytokine. 2004 Feb 21;25(4):172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2003.11.013. Cytokine. 2004. PMID: 15162834
-
Neonatal immune responses to TLR2 stimulation: influence of maternal atopy on Foxp3 and IL-10 expression.Respir Res. 2006 Mar 21;7(1):40. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-40. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 16551363 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary intake and blood concentrations of antioxidants and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies.Am J Clin Nutr. 2018 Nov 1;108(5):1069-1091. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy097. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30475962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nutrition and respiratory health--feature review.Nutrients. 2015 Mar 5;7(3):1618-43. doi: 10.3390/nu7031618. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 25751820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asthma, allergy and vitamin E: Current and future perspectives.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Feb 1;179:388-402. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.10.037. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 34785320 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition and Immunity in Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury.Nutrients. 2022 Jul 1;14(13):2747. doi: 10.3390/nu14132747. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurological damages in COVID-19 patients: Mechanisms and preventive interventions.MedComm (2020). 2023 Apr 6;4(2):e247. doi: 10.1002/mco2.247. eCollection 2023 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37035134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Clinical Indications and Current Challenges for Chromatographic Measurement.Clin Biochem Rev. 2016 Feb;37(1):27-47. Clin Biochem Rev. 2016. PMID: 27057076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barker R.N., Burney P.G., Devereux G., Hardiman M., Holt P.G., O’Donnell M., Platts-Mills T.A., Seaton A., Strachan D.P., Weiss S.T., et al. The increase in allergic disease: Environment and susceptibility. Proceedings of a Symposium held at the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 4th June 2002. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2003;33:394–406. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01621.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Malmberg K., Lenkei R., Petersson M., Ohlum T., Ichihara F., Glimelius B., Frödin J.E., Masucci G., Kiessling R. A short-term dietary supplementation of high doses of vitamin E increases T helper 1 cytokine production in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002;8:1772–1778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

