The changing immune system in sepsis: is individualized immuno-modulatory therapy the answer?
- PMID: 24067565
- PMCID: PMC3916383
- DOI: 10.4161/viru.26516
The changing immune system in sepsis: is individualized immuno-modulatory therapy the answer?
Abstract
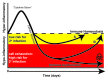
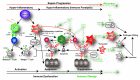
Sepsis remains the leading cause of death in most intensive care units. Advances in understanding the immune response to sepsis provide the opportunity to develop more effective therapies. The immune response in sepsis can be characterized by a cytokine-mediated hyper-inflammatory phase, which most patients survive, and a subsequent immune-suppressive phase. Patients fail to eradicate invading pathogens and are susceptible to opportunistic organisms in the hypo-inflammatory phase. Many mechanisms are responsible for sepsis-induced immuno-suppression, including apoptotic depletion of immune cells, increased T regulatory and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and cellular exhaustion. Currently in clinical trial for sepsis are granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor and interferon gamma, immune-therapeutic agents that boost patient immunity. Immuno-adjuvants with promise in clinically relevant animal models of sepsis include anti-programmed cell death-1 and interleukin-7. The future of immune therapy in sepsis will necessitate identification of the immunologic phase using clinical and laboratory parameters as well as biomarkers of innate and adaptive immunity.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; cell exhaustion; immune suppression; immune therapy; sepsis.
Figures
References
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, et al. International Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee. American Association of Critical-Care Nurses. American College of Chest Physicians. American College of Emergency Physicians. Canadian Critical Care Society. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. European Respiratory Society. International Sepsis Forum. Japanese Association for Acute Medicine. Japanese Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Society of Critical Care Medicine. Society of Hospital Medicine. Surgical Infection Society. World Federation of Societies of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:296–327. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000298158.12101.41. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
