Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: vascular or viral?
- PMID: 24067949
- PMCID: PMC4068115
- DOI: 10.1177/0194599813506546
Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: vascular or viral?
Abstract
Objective: To demonstrate that sudden sensorineural hearing loss is possibly of viral origin rather than vascular.
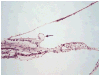
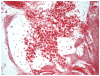
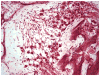
Study design: The histopathologic morphology in 7 temporal bones with known vascular impairment due to surgical interventions was compared with that of 11 bones with a history of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL). Attention was paid to the spiral ligament, stria vascularis, organ of Corti hair cells, tectorial membrane, ganglion cell population, and degree of perilymph fibrosis and the auditory nerve.
Setting: A temporal bone laboratory that has been in operation for more than 50 years and includes a database consisting of clinical and histopathological information that facilitates quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Subjects: Eight hundred forty-nine individuals who pledged their temporal bones for scientific study, of which 18 were selected for this study by means of the database criteria of sudden sensorineural hearing loss and postmiddle fossa and retro sigmoid sinus tumor removal or vestibular nerve section.
Results: Sudden sensorineural hearing loss bones exhibited no perilymph fibrosis compared with 6 of 7 vascular cases with fibrosis (P ≤ .001), exhibited less loss of ganglion cells (P ≤ .026), exhibited greater survival of spiral ligament (P ≤ .029), and averaged twice the survival of hair cells and more widespread tectorial membrane abnormalities.
Conclusion: Analysis of human temporal bones from patients with a sudden sensorineural hearing loss does not support a vascular insufficiency but is more suggestive of a viral etiology.
Keywords: sudden sensorineural; vascular; viral.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
Competing interests: None.
Sponsorships: None.
Figures

References
-
- Lindsay JR, Hemenway WG. Inner ear pathology due to measles. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1954;63:754–771. - PubMed
-
- Lindsay JR, Davey PR, Ward PH. Inner ear pathology in deafness due to mumps. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1960;69:918–935. - PubMed
-
- Van Dishoeck HAE, Bierman TA. Sudden perceptive deafness and viral infection: report of the first one hundred patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1957;66:963–980. - PubMed
-
- Stokroos RJ, Albers FW, Krikke AP, Casselman JW. Magnetic resonance imaging of the inner ear in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1998;255:433–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

