Inhibition of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection by anti-CD26 monoclonal antibody
- PMID: 24067970
- PMCID: PMC3838260
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02448-13
Inhibition of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection by anti-CD26 monoclonal antibody
Abstract
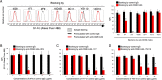
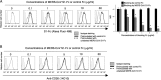
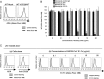
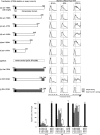
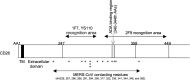
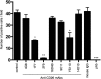
We identified the domains of CD26 involved in the binding of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) using distinct clones of anti-CD26 monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). One clone, named 2F9, almost completely inhibited viral entry. The humanized anti-CD26 MAb YS110 also significantly inhibited infection. These findings indicate that both 2F9 and YS110 are potential therapeutic agents for MERS-CoV infection. YS110, in particular, is a good candidate for immediate testing as a therapeutic modality for MERS.
Figures


References
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. 2012. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 367:1814–1820 - PubMed
-
- Enserink M. 2013. New coronavirus reveals some of its secrets. Science 340:17–18 - PubMed
-
- de Groot RJ, Baker SC, Baric RS, Brown CS, Drosten C, Enjuanes L, Fouchier RA, Galiano M, Gorbalenya AE, Memish Z, Perlman S, Poon LL, Snijder EJ, Stephens GM, Woo PC, Zaki AM, Zambon M, Ziebuhr J. 2013. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): announcement of the Coronavirus Study Group. J. Virol. 87:7790–7792 - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO 2013. Novel coronavirus infection—update. http://www.who.int/csr/don/2013_09_17_ncov/en/index.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

