Severe multi-resistant pemphigus vulgaris: prolonged remission with a single cycle of rituximab
- PMID: 24068143
- PMCID: PMC3760947
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20131990
Severe multi-resistant pemphigus vulgaris: prolonged remission with a single cycle of rituximab
Abstract
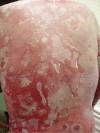
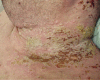
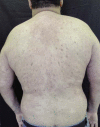
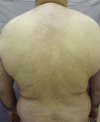
Pemphigus vulgaris is an autoimmune bullous disease whose therapy is based on systemic corticosteroids, with or without immunosuppressants. Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody of the IgG class, directed at a specific CD20 B cell surface antigen, used in pemphigus vulgaris empirically since 2002, with success in 90% of the cases and long periods of remission. Male patient, 33 years old, diagnosed with pemphigus vulgaris, confirmed by histopathology and direct immunofluorescence. He was treated for seven months with numerous treatments, including immunosuppressive drugs, with an unsatisfactory response, until he had complete remission with the use of rituximab. During a 34-month follow-up period, the patient presented a slight clinical relapse, which was successfully controlled with prednisone in a daily dose of 120 mg, soon reduced to 20mg.
Pênfigo Vulgar é uma doença bolhosa auto-imune, cuja terapêutica é baseada em corticoesteróides sistêmicos, associados ou não a imunossupressores. Rituximabe é um anticorpo monoclonal quimérico da classe IgG direcionado a um antígeno CD20 de superfície celular específico da célula B, usado em pênfigo vulgar desde 2002, com sucesso em 90% e longos períodos de remissão. Paciente masculino, 33 anos, diagnóstico de pênfigo vulgar, confirmado por histopatologia e imunofluorescência direta. Durante 7 meses, recebeu inúmeros tratamentos com imunossupressores, apresentando resposta insatisfatória e progressão da doença, até que logo após a introdução de rituximabe teve completa remissão. Durante um acompanhamento de 34 meses, apresentou leve recidiva clínica, controlada com prednisona 120mg/dia, rapidamente reduzida e em uso atual de Prednisona 20mg/dia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Hertl M, Zillikens D, Borradori L, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Burckhard H, Eming R, et al. Recommendations for the use of rituximab (anti-CD20 antibody) in the treatment of autoimmune bullous skin diseases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2008;6:366–373. - PubMed
-
- Goebeler M, Herzog S, Bröcker EB, Zillikens D. Rapid response of treatment-resistant pemphigus foliaceus to the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:899–901. - PubMed
-
- Daniel BS, Murrell DF, Joly P. Rituximab and its use in autoimmune bullous disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:571–575. - PubMed
-
- Mouquet H, Musette P, Gougeon ML, Jacquot S, Lemercier B, Lim A, et al. B-cell depletion immunotherapy in pemphigus: effects on cellular and humoral immune responses. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:2859–2869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical