Effectiveness of diaphragmatic stimulation with single-channel electrodes in rabbits
- PMID: 24068272
- PMCID: PMC4075865
- DOI: 10.1590/S1806-37132013000400014
Effectiveness of diaphragmatic stimulation with single-channel electrodes in rabbits
Abstract
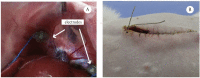
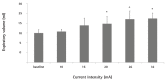
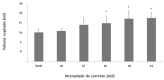
Every year, a large number of individuals become dependent on mechanical ventilation because of a loss of diaphragm function. The most common causes are cervical spinal trauma and neuromuscular diseases. We have developed an experimental model to evaluate the performance of electrical stimulation of the diaphragm in rabbits using single-channel electrodes implanted directly into the muscle. Various current intensities (10, 16, 20, and 26 mA) produced tidal volumes above the baseline value, showing that this model is effective for the study of diaphragm performance at different levels of electrical stimulation.
A cada ano um grande número de pessoas perde a função do diafragma tornando-se dependentes de ventilação mecânica. As principais causas são o trauma raquimedular da região cervical e as doenças neuromusculares. Desenvolvemos um modelo experimental para avaliar o desempenho da estimulação elétrica do diafragma em coelhos com eletrodos monocanais implantados diretamente neste músculo. Foram aplicadas diferentes intensidades de correntes (10, 16, 20 e 26 mA), as quais geraram volumes correntes acima dos valores basais, mostrando que este modelo é eficaz para estudar o desempenho do diafragma sob diferentes tipos de estimulação elétrica
Figures

References
-
- Oliveira AS, Pereira RD. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): three letters that change the people's life. For ever. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2009;67(3A):750–782. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0004-282X2009000400040 PMid:19722069 - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Statistics 2009. Geneva: World Health Organization; [cited 2010 Apr 01]. 149p. [homepage on the Internet] [Adobe Acrobat document]. Available from: http://www.who.int/whosis/whostat/EN_WHS09_Full.pdf.
-
- Glenn WW, Holcomb WG, Gee JB, Rath R. Central hypoventilation; long-term ventilatory assistance by radiofrequency electrophrenic respiration. Ann Surg. 1970;172(4):755–773. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000658-197010000-00020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Geddes LA, Voorhees WD, Babbs CF, Deford JA. Electroventilation. Am J Emerg Med. 1985;3(4):337–339. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0735-6757(85)90061-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geddes LA, Voorhees WD, Lagler R, Riscili C, Foster K, Bourland JD. Electrically produced artificial ventilation. Med Instrum. 1988;22(5):263–271. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

