Erectogenic and Aphrodisiac Effects of Butea frondosa Koenig ex Roxb. in Rats: Involvement of Enzyme Inhibition
- PMID: 24069061
- PMCID: PMC3773451
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/874894
Erectogenic and Aphrodisiac Effects of Butea frondosa Koenig ex Roxb. in Rats: Involvement of Enzyme Inhibition
Abstract
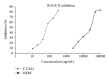
Butea frondosa Koenig ex Roxb. (BF) is traditionally used to manage male sexual disorders including erectile dysfunction (ED). Methanol extract of BF (bark) inhibited Rho-kinase 2 (ROCK-II) enzyme activity in vitro with an IC50 of 20.29 ± 1.83 μ g/mL. The relaxant effect of methanol extract of BF (MEBF) was studied on phenylephrine precontracted corpus cavernosum smooth muscle (CCSM) isolated from young rats. The effect of MEBF treatment on sexual behaviour of both young (5 month) and aged (24 month) rats was also studied in addition to the influence on smooth muscle, collagen (collagen-I and -III) level in penis, and sperm characteristics of young and aged rats. MEBF relaxed CCSM up to 21.77 ± 2.57% and increased sexual behavior of young and aged rats. This increase in sexual function could be attributed to ROCK-II inhibition and increase in ratio of smooth muscle to collagen level in rat penile tissue. Increased sperm production and decreased defective sperms in young and aged rats corroborate the usefulness of Butea frondosa in male infertility in addition to ED.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of Cinnamomum cassia methanol extract and sildenafil on arginase and sexual function of young male Wistar rats.J Sex Med. 2014 Jun;11(6):1475-83. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12535. Epub 2014 Apr 23. J Sex Med. 2014. PMID: 24758372
-
Screening for Rho-kinase 2 inhibitory potential of Indian medicinal plants used in management of erectile dysfunction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Dec 18;144(3):483-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.045. Epub 2012 Oct 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23043981
-
Aphrodisiac activity of Butea frondosa Koen. ex Roxb. extract in male rats.Phytomedicine. 2004 Feb;11(2-3):165-8. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00343. Phytomedicine. 2004. PMID: 15070167
-
Additive effects of the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 and vardenafil on relaxation of the corpus cavernosum tissue of patients with erectile dysfunction and clinical phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor failure.BJU Int. 2017 Feb;119(2):325-332. doi: 10.1111/bju.13691. Epub 2016 Nov 21. BJU Int. 2017. PMID: 27763717
-
Update on corpus cavernosum smooth muscle contractile pathways in erectile function: a role for testosterone?J Sex Med. 2011 Jul;8(7):1865-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02218.x. Epub 2011 Feb 16. J Sex Med. 2011. PMID: 21324096 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Intracorporeal Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (hADSCs) on Corpora Cavernosa Transforming Growth Factor β1 (TGFβ1) and Collagen Type I Concentration in Wistar Rat Priapism Model.Res Rep Urol. 2020 Feb 5;12:21-27. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S232303. eCollection 2020. Res Rep Urol. 2020. PMID: 32104667 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of diabetes on male sexual function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Protective role of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jul;115:108897. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108897. Epub 2019 May 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31102913 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of ellagic acid and sildenafil in diabetes-induced sexual dysfunction.Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Aug;10(Suppl 3):S581-7. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.139790. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014. PMID: 25298678 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Cinnamomum cassia Blume. in age induced sexual dysfunction of rats.J Young Pharm. 2013 Dec;5(4):148-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jyp.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Dec 9. J Young Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24563594 Free PMC article.
-
Antifertility effect of methanolic extract of Butea monosperma (Lam.) Taub. flower in male albino rats.Ayu. 2021 Jan-Mar;42(1):57-66. doi: 10.4103/ayu.AYU_91_20. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Ayu. 2021. PMID: 36743278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. Impotence. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 1993;270(1):83–90. - PubMed
-
- Andersson KE. Pharmacology of penile erection. Pharmacological Reviews. 2001;53(3):417–450. - PubMed
-
- Doumas M, Tsakiris A, Douma S, et al. Factors affecting the increased prevalence of erectile dysfunction in greek hypertensive compared with normotensive subjects. Journal of Andrology. 2006;27(3):469–477. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

