Intranasal delivery of plasma and platelet growth factors using PRGF-Endoret system enhances neurogenesis in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24069173
- PMCID: PMC3777974
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073118
Intranasal delivery of plasma and platelet growth factors using PRGF-Endoret system enhances neurogenesis in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
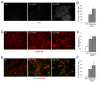
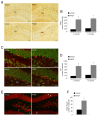
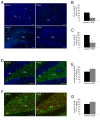
Neurodegeneration together with a reduction in neurogenesis are cardinal features of Alzheimer's disease (AD) induced by a combination of toxic amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) and a loss of trophic factor support. Amelioration of these was assessed with diverse neurotrophins in experimental therapeutic approaches. The aim of this study was to investigate whether intranasal delivery of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret), an autologous pool of morphogens and proteins, could enhance hippocampal neurogenesis and reduce neurodegeneration in an amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 (APP/PS1) mouse model. Neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions were firstly evident in primary neuronal cultures, where cell proliferation and survival were augmented by Endoret treatment. Translation of these effects in vivo was assessed in wild type and APP/PS1 mice, where neurogenesis was evaluated using 5-bromodeoxyuridine (BdrU), doublecortin (DCX), and NeuN immunostaining 5 weeks after Endoret administration. The number of BrdU, DCX, and NeuN positive cell was increased after chronic treatment. The number of degenerating neurons, detected with fluoro Jade-B staining was reduced in Endoret-treated APP/PS1 mice at 5 week after intranasal administration. In conclusion, Endoret was able to activate neuronal progenitor cells, enhancing hippocampal neurogenesis, and to reduce Aβ-induced neurodegeneration in a mouse model of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM (2010) Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 362: 329-344. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0909142. PubMed: 20107219. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang C, McNeil E, Dressler L, Siman R (2007) Long-lasting impairment in hippocampal neurogenesis associated with amyloid deposition in a knock-in mouse model of familial Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 204: 77-87. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.09.018. PubMed: 17070803. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verret L, Jankowsky JL, Xu GM, Borchelt DR, Rampon C (2007) Alzheimer’s-type amyloidosis in transgenic mice impairs survival of newborn neurons derived from adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci 27: 6771-6780. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5564-06.2007. PubMed: 17581964. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ermini FV, Grathwohl S, Radde R, Yamaguchi M, Staufenbiel M et al. (2008) Neurogenesis and alterations of neural stem cells in mouse models of cerebral amyloidosis. Am J Pathol 172: 1520-1528. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.060520. PubMed: 18467698. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez JJ, Jones VC, Tabuchi M, Allan SM, Knight EM et al. (2008) Impaired adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLOS ONE 3: e2935. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002935. PubMed: 18698410. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

