Enhanced production of recombinant secretory proteins in Pichia pastoris by optimizing Kex2 P1' site
- PMID: 24069404
- PMCID: PMC3777899
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075347
Enhanced production of recombinant secretory proteins in Pichia pastoris by optimizing Kex2 P1' site
Abstract
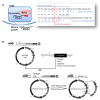
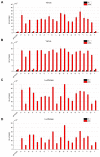
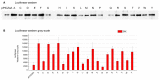
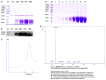
Pichiapastoris is one of the most widely used expression systems for the production of recombinant secretory proteins. Its universal application is, however, somewhat hampered by its unpredictable yields for different heterologous proteins, which is now believed to be caused in part by their varied efficiencies to traffic through the host secretion machinery. The yeast endoprotease Kex2 removes the signal peptides from pre-proteins and releases the mature form of secreted proteins, thus, plays a pivotal role in the yeast secretory pathways. In this study, we found that the yields of many recombinant proteins were greatly influenced by Kex2 P1' site residues and the optimized P1's amino acid residue could largely determine the final amount of secretory proteins synthesized and secreted. A further improvement of secretory yield was achieved by genomic integration of additional Kex2 copies, which again highlighted the importance of Kex2 cleavage to the production of recombinant secretory proteins in Pichia yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modifications in the Kex2 P1' cleavage site in the α-MAT secretion signal lead to higher production of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in Pichia pastoris.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Oct 16;37(11):197. doi: 10.1007/s11274-021-03167-3. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34654975
-
Improving the Secretory Expression of an -Galactosidase from Aspergillus niger in Pichia pastoris.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 22;11(8):e0161529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161529. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27548309 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation on the processing and improving the cleavage efficiency of furin cleavage sites in Pichia pastoris.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Nov 8;17(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-1020-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 30409181 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris: a useful experimental tool in protein engineering and production.J Mol Recognit. 2005 Mar-Apr;18(2):119-38. doi: 10.1002/jmr.687. J Mol Recognit. 2005. PMID: 15565717 Review.
-
Pichia pastoris: A highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Sep;235(9):5867-5881. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29583. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32057111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enabling low cost biopharmaceuticals: high level interferon alpha-2b production in Trichoderma reesei.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 Jun 10;15(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0508-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 27287473 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Modification of Kex2 P1' Site Enhances Expression and Druggability of Fungal Defensin.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 20;12(4):786. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040786. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107149 Free PMC article.
-
Differential role of segments of α-mating factor secretion signal in Pichia pastoris towards granulocyte colony-stimulating factor emerging from a wild type or codon optimized copy of the gene.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Oct 29;19(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01460-8. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 33121493 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular optimization of rabies virus glycoprotein expression in Pichia pastoris.Microb Biotechnol. 2016 May;9(3):355-68. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12350. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Microb Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26880068 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Transcription Factors for Tuneable Gene Expression in Pichia pastoris.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 9;9:676900. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.676900. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34434924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goodman M (2009) Market watch: Sales of biologics to show robust growth through to 2013. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8: 837. doi:10.1038/nrd3040. PubMed: 19876035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sheridan C (2010) Fresh from the biologic pipeline-2009. Nat Biotechnol 28: 307-310. doi:10.1038/nbt0410-307. PubMed: 20379168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2005) Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast 22: 249-270. doi:10.1002/yea.1208. PubMed: 15704221. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li P, Anumanthan A, Gao XG, Ilangovan K, Suzara VV et al. (2007) Expression of recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 142: 105-124. doi:10.1007/s12010-007-0003-x. PubMed: 18025573. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cos O, Ramón R, Montesinos JL, Valero F (2006) Operational strategies, monitoring and control of heterologous protein production in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris under different promoters: a review. Microb Cell Factories 5: 17. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-5-S1-S17. PubMed: 16600031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

