Serotonin 2B receptor (5-HT2B R) signals through prostacyclin and PPAR-ß/δ in osteoblasts
- PMID: 24069449
- PMCID: PMC3775737
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075783
Serotonin 2B receptor (5-HT2B R) signals through prostacyclin and PPAR-ß/δ in osteoblasts
Abstract
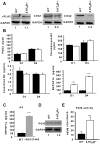
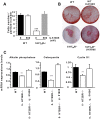
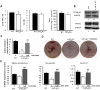
Osteoporosis is due to an imbalance between decreased bone formation by osteoblasts and increased resorption by osteoclasts. Deciphering factors controlling bone formation is therefore of utmost importance for the understanding and the treatment of osteoporosis. Our previous in vivo results showed that bone formation is reduced in the absence of the serotonin receptor 5-HT2B, causing impaired osteoblast proliferation, recruitment, and matrix mineralization. In this study, we investigated the signaling pathways responsible for the osteoblast defect in 5-HT2BR(-/-) mice. Notably, we investigated the phospholipase A2 pathway and synthesis of eicosanoids in 5-HT2BR(-/-) compared to wild type (WT) osteoblasts. Compared to control osteoblasts, the lack of 5-HT2B receptors was only associated with a 10-fold over-production of prostacyclin (PGI2). Also, a specific prostacyclin synthase inhibitor (U51605) rescued totally osteoblast aggregation and matrix mineralization in the 5-HT2BR(-/-) osteoblasts without having any effect on WT osteoblasts. Prostacyclin is the endogenous ligand of the nuclear peroxisome proliferator activated receptor ß/δ (PPAR-ß/δ), and its inhibition in 5-HT2BR(-/-) cells rescued totally the alkaline phosphatase and osteopontin mRNA levels, cell-cell adhesion, and matrix mineralization. We conclude that the absence of 5-HT2B receptors leads to the overproduction of prostacyclin, inducing reduced osteoblast differentiation due to PPAR-ß/δ -dependent target regulation and defective cell-cell adhesion and matrix mineralization. This study thus reveals a previously unrecognized cell autonomous osteoblast defect in the absence of 5-HT2BR and highlights a new pathway linking 5-HT2B receptors and nuclear PPAR- ß/δ via prostacyclin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibitors of Growth 1b Suppresses Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-β/δ Expression Through Downregulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in Osteoblast Differentiation.DNA Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;35(4):184-91. doi: 10.1089/dna.2015.3020. Epub 2016 Feb 5. DNA Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26849833 Free PMC article.
-
PPARβ/δ governs Wnt signaling and bone turnover.Nat Med. 2013 May;19(5):608-13. doi: 10.1038/nm.3146. Epub 2013 Mar 31. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23542786
-
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and rosiglitazone synergistically enhance osteoblast-mediated mineralization.Gene. 2013 Jan 10;512(2):438-43. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.07.051. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Gene. 2013. PMID: 22967709
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta as a therapeutic target for metabolic diseases.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005 Aug;9(4):861-73. doi: 10.1517/14728222.9.4.861. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005. PMID: 16083348 Review.
-
Emerging roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta/delta in inflammation.Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Nov;124(2):141-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.06.011. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19615407 Review.
Cited by
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; Pharmacology and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Jan;73(1):310-520. doi: 10.1124/pr.118.015552. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33370241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Cause Fractures?Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016 Oct;14(5):211-8. doi: 10.1007/s11914-016-0322-3. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016. PMID: 27495351 Review.
-
Orotracheal treprostinil administration attenuates bleomycin-induced lung injury, vascular remodeling, and fibrosis in mice.Pulm Circ. 2019 Nov 15;9(4):2045894019881954. doi: 10.1177/2045894019881954. eCollection 2019 Oct-Dec. Pulm Circ. 2019. PMID: 31819797 Free PMC article.
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) affect murine bone lineage cells.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 15;255:117827. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117827. Epub 2020 May 22. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32450170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hannon J, Hoyer D (2008) Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Behav Brain Res 195: 198–213. - PubMed
-
- Nebigil CG, Hickel P, Messaddeq N, Vonesch JL, Douchet MP, et al. (2001) Ablation of serotonin 5-HT(2B) receptors in mice leads to abnormal cardiac structure and function. Circulation 103: 2973–2979. - PubMed
-
- Launay JM, Herve P, Callebert J, Mallat Z, Collet C, et al. (2012) Serotonin 5-HT2B receptors are required for bone-marrow contribution to pulmonary arterial hypertension. Blood 119: 1772–1780. - PubMed
-
- Lesurtel M, Graf R, Aleil B, Walther DJ, Tian Y, et al. (2006) Platelet-derived serotonin mediates liver regeneration. Science 312: 104–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

