The involvement of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in chronic inflammatory skin disease atopic dermatitis
- PMID: 24069552
- PMCID: PMC3772104
- DOI: 10.4161/jkst.24137
The involvement of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in chronic inflammatory skin disease atopic dermatitis
Abstract
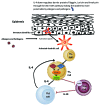
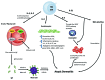
Atopic dermatitis (AD), a common chronic inflammatory skin disease, is characterized by inflammatory cell skin infiltration. The JAK-STAT pathway has been shown to play an essential role in the dysregulation of immune responses in AD, including the exaggeration of Th2 cell response, the activation of eosinophils, the maturation of B cells, and the suppression of regulatory T cells (Tregs). In addition, the JAK-STAT pathway, activated by IL-4, also plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of AD by upregulating epidermal chemokines, pro-inflammatroy cytokines, and pro-angiogenic factors as well as by downregulating antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and factors responsible for skin barrier function. In this review, we will highlight the recent advances in our understanding of the JAK-STAT pathway in the pathogenesis of AD.
Keywords: JAK-STAT; Th2; atopic dermatitis; inflammation; skin.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
