Genome mining reveals the genus Xanthomonas to be a promising reservoir for new bioactive non-ribosomally synthesized peptides
- PMID: 24069909
- PMCID: PMC3849588
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-658
Genome mining reveals the genus Xanthomonas to be a promising reservoir for new bioactive non-ribosomally synthesized peptides
Abstract
Background: Various bacteria can use non-ribosomal peptide synthesis (NRPS) to produce peptides or other small molecules. Conserved features within the NRPS machinery allow the type, and sometimes even the structure, of the synthesized polypeptide to be predicted. Thus, bacterial genome mining via in silico analyses of NRPS genes offers an attractive opportunity to uncover new bioactive non-ribosomally synthesized peptides. Xanthomonas is a large genus of Gram-negative bacteria that cause disease in hundreds of plant species. To date, the only known small molecule synthesized by NRPS in this genus is albicidin produced by Xanthomonas albilineans. This study aims to estimate the biosynthetic potential of Xanthomonas spp. by in silico analyses of NRPS genes with unknown function recently identified in the sequenced genomes of X. albilineans and related species of Xanthomonas.
Results: We performed in silico analyses of NRPS genes present in all published genome sequences of Xanthomonas spp., as well as in unpublished draft genome sequences of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strain BAI3 and Xanthomonas spp. strain XaS3. These two latter strains, together with X. albilineans strain GPE PC73 and X. oryzae pv. oryzae strains X8-1A and X11-5A, possess novel NRPS gene clusters and share related NRPS-associated genes such as those required for the biosynthesis of non-proteinogenic amino acids or the secretion of peptides. In silico prediction of peptide structures according to NRPS architecture suggests eight different peptides, each specific to its producing strain. Interestingly, these eight peptides cannot be assigned to any known gene cluster or related to known compounds from natural product databases. PCR screening of a collection of 94 plant pathogenic bacteria indicates that these novel NRPS gene clusters are specific to the genus Xanthomonas and are also present in Xanthomonas translucens and X. oryzae pv. oryzicola. Further genome mining revealed other novel NRPS genes specific to X. oryzae pv. oryzicola or Xanthomonas sacchari.
Conclusions: This study revealed the significant potential of the genus Xanthomonas to produce new non-ribosomally synthesized peptides. Interestingly, this biosynthetic potential seems to be specific to strains of Xanthomonas associated with monocotyledonous plants, suggesting a putative involvement of non-ribosomally synthesized peptides in plant-bacteria interactions.
Figures

 : tRNA. Orientation of the tag indicates the orientation of the tRNA gene in the genomic regions. Amino acid specificity of each tRNA is indicated above or below each tag according to the orientation of the tRNA gene. ???? : undetermined sequence located between contigs. Two contigs separated by this tag may be located in two different genomic regions (they are not necessarily contiguous).
: tRNA. Orientation of the tag indicates the orientation of the tRNA gene in the genomic regions. Amino acid specificity of each tRNA is indicated above or below each tag according to the orientation of the tRNA gene. ???? : undetermined sequence located between contigs. Two contigs separated by this tag may be located in two different genomic regions (they are not necessarily contiguous).  : this tag indicates that corresponding genomic regions are not contiguous. Data on strain CFBP4834-R of X. axonopodis pv. phaseoli were obtained from an unpublished finished genome sequence (M.-A. Jacques, personal communication).
: this tag indicates that corresponding genomic regions are not contiguous. Data on strain CFBP4834-R of X. axonopodis pv. phaseoli were obtained from an unpublished finished genome sequence (M.-A. Jacques, personal communication).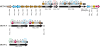
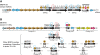

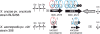
 : tRNA. Orientation of the tag indicates the orientation of the tRNA gene in the genomic regions. Amino acid specificity of each tRNA is indicated above or below each tag according to the orientation of the tRNA gene. IS: insertion sequence. Dotted arrows: pseudogenes. Dotted and incomplete circles: incomplete and non-functional modules.
: tRNA. Orientation of the tag indicates the orientation of the tRNA gene in the genomic regions. Amino acid specificity of each tRNA is indicated above or below each tag according to the orientation of the tRNA gene. IS: insertion sequence. Dotted arrows: pseudogenes. Dotted and incomplete circles: incomplete and non-functional modules.References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

