Oral caffeine during voluntary exercise markedly inhibits skin carcinogenesis and decreases inflammatory cytokines in UVB-treated mice
- PMID: 24070239
- PMCID: PMC3830615
- DOI: 10.1080/01635581.2013.812224
Oral caffeine during voluntary exercise markedly inhibits skin carcinogenesis and decreases inflammatory cytokines in UVB-treated mice
Abstract
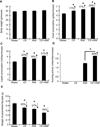
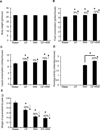
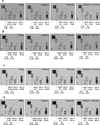
Ultraviolet B (UVB)-pretreated SKH-1 mice were treated with water, caffeine (0.1 mg/ml), voluntary running wheel exercise (RW) or caffeine together with RW for 14 wk. Treatment of the mice with caffeine, RW, or caffeine plus RW decreased skin tumors per mouse by 27%, 35%, and 62%, respectively, and the tumor volume per mouse was decreased by 61%, 70%, and 85%, respectively. In mechanistic studies, mice were treated with water, caffeine, RW, or caffeine plus RW for 2 wk prior to a single irradiation with UVB. Caffeine plus RW increased RW activity by 22% when compared with RW alone. Caffeine ingestion was not significantly different between groups. Treatment of mice with caffeine plus RW for 2 wk decreased the weight of the parametrial fat pads and stimulated the formation of UVB-induced apoptosis to a greater extent than treatment with caffeine or RW alone. An antibody array revealed that caffeine plus RW administered to mice fed a high-fat diet and irradiated with UVB decreased the epidermal levels of lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine, soluble TNF alpha receptor-1, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1γ. Overall, caffeine during RW exerts a stronger effect than either treatment alone for decreasing tissue fat, increasing UVB-induced apoptosis, lowering the levels of cytokines associated with inflammation and for inhibiting UVB-induced carcinogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Lu Y-P, Lou L-R, Lin Y, Shih WJ, Huang M-T, et al. Inhibitory effects of orally administered green tea, black tea, and caffeine on skin carcinogenesis in mice previously treated with ultraviolet B light (high-risk mice): relationship to decreased tissue fat. Cancer Research. 2001;61:5002–5009. - PubMed
-
- Lu YP, Lou YR, Li XH, Xie JG, Brash D, et al. Stimulatory effect of oral administration of green tea or caffeine on ultraviolet light-induced increases in epidermal wild-type p53, p21(WAF1/CIP1), and apoptotic sunburn cells in SKH-1 mice. Cancer Research. 2000;60:4785–4791. - PubMed
-
- Michna L, Lu YP, Lou YR, Wagner GC, Conney AH. Stimulatory effect of oral administration of green tea and caffeine on locomotor activity in SKH-1 mice. Life Sciences. 2003;73:1383–1392. - PubMed
-
- Lou YR, Lu YP, Xie JG, Huang MT, Conney AH. Effects of oral administration of tea, decaffeinated tea, and caffeine on the formation and growth of tumors in high-risk SKH-1 mice previously treated with ultraviolet B light. Nutrition and Cancer. 1999;33:146–153. - PubMed
-
- Michna L, Wagner GC, Lou YR, Xie JG, Peng QY, et al. Inhibitory effects of voluntary running wheel exercise on UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis in SKH-1 mice. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:2108–2115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
