Increased resistin in brain dead organ donors is associated with delayed graft function after kidney transplantation
- PMID: 24070260
- PMCID: PMC3849100
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-233
Increased resistin in brain dead organ donors is associated with delayed graft function after kidney transplantation
Abstract
Introduction: Resistin increases during several inflammatory diseases and after intracerebral bleeding or head trauma. Resistin activates the endothelium and may initiate an inflammatory response. No data are available on resistin in brain dead donors (DBD) that regularly manifest a pronounced inflammatory state.
Methods: We analyzed plasma resistin in 63 DBDs and correlated results with donor variables and the postoperative course following kidney transplantation using organs from these donors. Endocan and monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1 were also studied. Twenty-six live kidney donors (LD) and the corresponding kidney transplantations were used as controls.
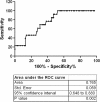
Results: DBDs had higher resistin (median/range 30.75 ng/ml, 5.41-173.6) than LD (7.71 ng/ml, 2.41-15.74, p < 0.0001). Resistin in DBD correlated with delayed graft function (DGF) in the kidney recipients (r = 0.321, p < 0.01); receiver operating characteristic curve revealed an area under the curve of 0.765 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.648-0.881, p < 0.01) and a cut-off value for resistin of 25 ng/ml; MCP-1 and endocan were higher in DBDs (p < 0.0001) but did not correlate with DGF or acute rejection. No relationship was found between the studied molecules and the postoperative course of LD kidney transplants.
Conclusions: High resistin levels in the DBD before organ retrieval are associated with DGF after kidney transplantation. The resistin increase seems related to the inflammatory state after brain death but not to the cause of death.
Figures

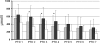
Similar articles
-
Circulating resistin levels are early and significantly increased in deceased brain dead organ donors, correlate with inflammatory cytokine response and remain unaffected by steroid treatment.J Transl Med. 2015 Jun 26;13:201. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0574-1. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26112052 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors: lack of impact of delayed graft function on post-transplant outcomes.Clin Transplant. 2011 Mar-Apr;25(2):255-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2010.01241.x. Clin Transplant. 2011. PMID: 20331689
-
Serum liver-type fatty acid-binding protein predicts recovery of graft function after kidney transplantation from donors after cardiac death.Clin Transplant. 2014 Jun;28(6):749-54. doi: 10.1111/ctr.12375. Epub 2014 May 23. Clin Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24750195
-
The impact of kidney donor profile index on delayed graft function and transplant outcomes: A single-center analysis.Clin Transplant. 2018 Mar;32(3):e13190. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13190. Clin Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29314286 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the brain-dead organ donor to predict immediate graft function in kidney recipients: a prospective, multicenter study.Anesthesiology. 2015 Jan;122(1):96-105. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000497. Anesthesiology. 2015. PMID: 25611655
Cited by
-
Adipocytokines in renal transplant recipients.Clin Kidney J. 2016 Jun;9(3):359-73. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfv156. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Clin Kidney J. 2016. PMID: 27274819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocan silencing induces programmed cell death in hepatocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):5333-5339. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6857. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29113167 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Kidney Transplantation and Immunosuppressive Therapy on Adipose Tissue Content and Adipocytokine Plasma Concentration-Preliminary Study.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 7;47(4):255. doi: 10.3390/cimb47040255. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699654 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating resistin levels are early and significantly increased in deceased brain dead organ donors, correlate with inflammatory cytokine response and remain unaffected by steroid treatment.J Transl Med. 2015 Jun 26;13:201. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0574-1. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26112052 Free PMC article.
-
High circulating endocan in chronic kidney disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 9;18(8):e0289710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289710. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37556458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nijboer WN, Schuurs TA, van der Hoeven JA, Fekken S, Wiersema-Buist J, Leuvenink HG, Hofker S, Homan van der Heide JJ, van Son WJ, Ploeg RJ. Effect of brain death on gene expression and tissue activation in human donor kidneys. Transplantation. 2004;78:978–986. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000135565.49535.60. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weiss S, Kotsch K, Francuski M, Reutzel-Selke A, Mantouvalou L, Klemz R, Kuecuek O, Jonas S, Wesslau C, Ulrich F. et al.Brain death activates donor organs and is associated with a worse I/R injury after liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:1584–1593. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01799.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Damman J, Seelen MA, Moers C, Daha MR, Rahmel A, Leuvenink HG, Paul A, Pirenne J, Ploeg RJ. Systemic complement activation in deceased donors is associated with acute rejection after renal transplantation in the recipient. Transplantation. 2011;92:163–169. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318222c9a0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

