IL-17A potentiates TNFα-induced secretion from human endothelial cells and alters barrier functions controlling neutrophils rights of passage
- PMID: 24072078
- PMCID: PMC4006128
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-013-1354-5
IL-17A potentiates TNFα-induced secretion from human endothelial cells and alters barrier functions controlling neutrophils rights of passage
Abstract
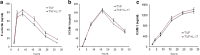
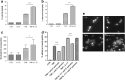
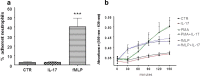
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) is an important pro-inflammatory cytokine that regulates leukocyte mobilization and recruitment. To better understand how IL-17A controls leukocyte trafficking across capillaries in the peripheral blood circulation, we used primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC) to investigate their secretory potential and barrier function when activated with IL-17A and TNFα. Activation by TNFα and IL-17A causes phosphorylation of p38 as well as IκBα whereby NFκB subsequently becomes phosphorylated, a mechanism that initiates transcription of adhesion molecules such as E-selectin. Members of the neutrophil-specific GRO-family chemokines were significantly up-regulated upon IL-17A stimulation on the mRNA and protein level, whereas all tested non-neutrophil-specific chemokines remained unchanged in comparison. Moreover, a striking synergistic effect in the induction of granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSF) was elicited when IL-17A was used in combination with TNFα, and IL-17A was able to significantly augment the levels of TNFα-induced E-selectin and ICAM-1. In accordance with this observation, IL-17A was able to markedly increase TNFα-induced neutrophil adherence to HDMEC monolayers in an in vitro adhesion assay. Using a trans-well migration assay with an HDMEC monolayer as a barrier, we here show that pre-stimulating the endothelial cells with TNFα and IL-17A together enhances the rate of neutrophil transmigration compared to TNFα or IL-17A alone. These results show that IL-17A and TNFα act in cooperation to facilitate neutrophil migration across the endothelial cell barrier. In addition, the synergistic actions of IL-17A with TNFα to secrete G-CSF appear to be important for mobilizing neutrophils from the bone marrow to the blood stream.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TNFα signals via p66(Shc) to induce E-Selectin, promote leukocyte transmigration and enhance permeability in human endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 2;8(12):e81930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081930. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349153 Free PMC article.
-
VCAM-1-, ELAM-1-, and ICAM-1-independent adhesion of melanoma cells to cultured human dermal microvascular endothelial cells.J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jan;98(1):79-85. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12495643. J Invest Dermatol. 1992. PMID: 1370233
-
Endothelial cell SHP-2 negatively regulates neutrophil adhesion and promotes transmigration by enhancing ICAM-1-VE-cadherin interaction.FASEB J. 2017 Nov;31(11):4759-4769. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700280R. Epub 2017 Jul 12. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28701303 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro inhibitory effect of IL-8 and other chemoattractants on neutrophil-endothelial adhesive interactions.J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2163-71. J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1381398
-
ICAM-1-mediated leukocyte adhesion is critical for the activation of endothelial LSP1.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 May 1;304(9):C895-904. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00297.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23447036
Cited by
-
Dietary salt, vascular dysfunction, and cognitive impairment.Cardiovasc Res. 2025 Apr 8;120(18):2349-2359. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvae229. Cardiovasc Res. 2025. PMID: 39429024 Review.
-
Effect of IL-17A on the immune response to pulmonary tuberculosis induced by high- and low-virulence strains of Mycobacterium bovis.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 18;19(7):e0307307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307307. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39024223 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin role in the regulation of endothelial cell pathological activation.Vasc Biol. 2021 Oct 18;3(1):R96-R105. doi: 10.1530/VB-21-0010. eCollection 2021. Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 34870094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic Acid: A New Old Friend of IL-17A in the Immune Pathogeny of Liver Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 15;12:691073. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.691073. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34211477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Effects of the Consumption of Passiflora setacea Juice on Metabolic Risk Factors and Gene Expression Profile in Humans.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 16;12(4):1104. doi: 10.3390/nu12041104. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32316129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahuja SK, Murphy PM. The CXC chemokines growth-regulated oncogene (GRO) alpha, GRObeta, GROgamma, neutrophil-activating peptide-2, and epithelial cell-derived neutrophil-activating peptide-78 are potent agonists for the type B, but not the type A, human interleukin-8 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20545–20550. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.34.20545. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andoh A, Takaya H, Makino J, Sato H, Bamba S, Araki Y, Hata K, Shimada M, Okuno T, Fujiyama Y, Bamba T. Cooperation of interleukin-17 and interferon-gamma on chemokine secretion in human fetal intestinal epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001;125:56–63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01588.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Awane M, Andres PG, Li DJ, Reinecker HC. NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is a common mediator of IL-17-, TNF-alpha-, and IL-1 beta-induced chemokine promoter activation in intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1999;162:5337–5344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

