Developmental origins of chronic renal disease: an integrative hypothesis
- PMID: 24073334
- PMCID: PMC3773449
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/346067
Developmental origins of chronic renal disease: an integrative hypothesis
Abstract
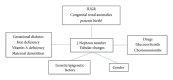
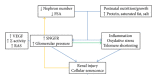
Cardiovascular diseases are one of the leading causes of mortality. Hypertension (HT) is one of the principal risk factors associated with death. Chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is probably underestimated, increases the risk and the severity of adverse cardiovascular events. It is now recognized that low birth weight is a risk factor for these diseases, and this relationship is amplified by a rapid catch-up growth or overfeeding during infancy or childhood. The pathophysiological and molecular mechanisms involved in the "early programming" of CKD are multiple and partially understood. It has been proposed that the developmental programming of arterial hypertension and chronic kidney disease is related to a reduced nephron endowment. However, this mechanism is still discussed. This review discusses the complex relationship between birth weight and nephron endowment and how early growth and nutrition influence long term HT and CKD. We hypothesize that fetal environment reduces moderately the nephron number which appears insufficient by itself to induce long term diseases. Reduced nephron number constitutes a "factor of vulnerability" when additional factors, in particular a rapid postnatal growth or overfeeding, promote the early onset of diseases through a complex combination of various pathophysiological pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Allender S, Scarborough P, Peto V, et al. European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics. 2008.
-
- Narayan KMV, Ali MK, Koplan JP. Global noncommunicable diseases: were worlds meet. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2010;363(13):1196–1198. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2007;298(17):2038–2047. - PubMed
-
- Gibson CM, Dumaine RL, Gelfand EV, et al. Association of glomerular filtration rate on presentation with subsequent mortality in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome; observations in 13307 patients in five TIMI trials. European Heart Journal. 2004;25(22):1998–2005. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

