Effects of repeated central administration of endothelin type A receptor antagonist on the development of neuropathic pain in rats
- PMID: 24073407
- PMCID: PMC3773389
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/529871
Effects of repeated central administration of endothelin type A receptor antagonist on the development of neuropathic pain in rats
Abstract
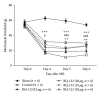
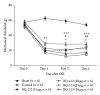
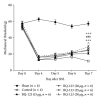
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) predominates in the endothelin family effectively in vascular tone control, mitogenesis, and neuromodulation. Its receptors are widespread in the central nervous system (CNS) associated with endogenous pain control, suggesting an important role of ET-1 in central pain processing. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of central ET-1 on the development of neuropathic pain behaviour by repeated intrathecal administration of endothelin type A receptor (ETAR) antagonist (BQ-123) in a sciatic nerve ligation (SNL) animal model. BQ-123 was administered intrathecally to rats at dosages 15 μg, 20 μg, 25 μg, and 30 μg, daily for 3 days. Mechanical allodynia was assessed daily 30 minutes before/after injection, 1 hour after injection of BQ-123 from post-SNL day 4 to day 6, and once on day 7 (without BQ-123 administration) before rats were sacrificed. Increasing trends of mechanical threshold were observed, and they reached significance at all dosages on post-SNL day 7 (P < 0.05 at dosage 15 μg and P < 0.001 at dosages 20 μg, 25 μg, and 30 μg) in comparison to control group. BQ-123 at dosage 30 μg showed the most stable and significant mechanical threshold rise. Repeated central administration of BQ-123 alleviated mechanical allodynia after SNL. Our results provide insight into the therapeutic strategies, including timing, against neuropathic pain development with ETAR antagonist.
Figures
References
-
- Berti-Mattera LN, Gariepy CE, Burke RM, Hall AK. Reduced expression of endothelin B receptors and mechanical hyperalgesia in experimental chronic diabetes. Experimental Neurology. 2006;201(2):399–406. - PubMed
-
- Naidoo V, Naidoo S, Mahabeer R, Raidoo DM. Cellular distribution of the endothelin system in the human brain. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy. 2004;27(2):87–98. - PubMed
-
- Giaid A, Gibson SJ, Herrero MT, et al. Topographical localisation of endothelin mRNA and peptide immunoreactivity in neurones of the human brain. Histochemistry. 1991;95(3):303–314. - PubMed
-
- Kurokawa K, Yamada H, Ochi J. Topographical distribution of neurons containing endothelin type A receptor in the rat brain. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1997;389(2):348–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

