The cell-cycle state of stem cells determines cell fate propensity
- PMID: 24074866
- PMCID: PMC3898746
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.031
The cell-cycle state of stem cells determines cell fate propensity
Erratum in
-
The Cell-Cycle State of Stem Cells Determines Cell Fate Propensity.Cell. 2014 Mar 13;156(6):1338. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.044. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Cell. 2014. PMID: 28898638 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells are fundamentally associated with cell-cycle progression to enable tissue specification, organ homeostasis, and potentially tumorigenesis. However, technical challenges have impaired the study of the molecular interactions coordinating cell fate choice and cell-cycle progression. Here, we bypass these limitations by using the FUCCI reporter system in human pluripotent stem cells and show that their capacity of differentiation varies during the progression of their cell cycle. These mechanisms are governed by the cell-cycle regulators cyclin D1-3 that control differentiation signals such as the TGF-β-Smad2/3 pathway. Conversely, cell-cycle manipulation using a small molecule directs differentiation of hPSCs and provides an approach to generate cell types with a clinical interest. Our results demonstrate that cell fate decisions are tightly associated with the cell-cycle machinery and reveal insights in the mechanisms synchronizing differentiation and proliferation in developing tissues.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
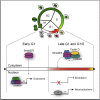
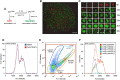
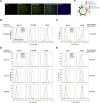

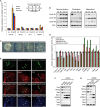
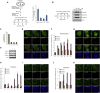
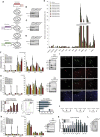



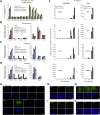
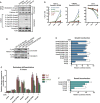
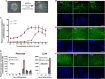
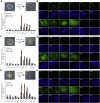

Comment in
-
G1 compartmentalization and cell fate coordination.Cell. 2013 Sep 26;155(1):13-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.015. Cell. 2013. PMID: 24074854
References
-
- Brons I.G., Smithers L.E., Trotter M.W., Rugg-Gunn P., Sun B., Chuva de Sousa Lopes S.M., Howlett S.K., Clarkson A., Ahrlund-Richter L., Pedersen R.A., Vallier L. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature. 2007;448:191–195. - PubMed
-
- Brown S., Teo A., Pauklin S., Hannan N., Cho C.H., Lim B., Vardy L., Dunn N.R., Trotter M., Pedersen R., Vallier L. Activin/Nodal signaling controls divergent transcriptional networks in human embryonic stem cells and in endoderm progenitors. Stem Cells. 2011;29:1176–1185. - PubMed
-
- Calder A., Roth-Albin I., Bhatia S., Pilquil C., Lee J.H., Bhatia M., Levadoux-Martin M., McNicol J., Russell J., Collins T. Lengthened G1 phase indicates differentiation status in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22:279–295. - PubMed
-
- Chng Z., Teo A., Pedersen R.A., Vallier L. SIP1 mediates cell-fate decisions between neuroectoderm and mesendoderm in human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6:59–70. - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Pratt T., Sharp L., Nichols J., Price D.J., Mason J.O. Embryonic stem cells and transgenic mice ubiquitously expressing a tau-tagged green fluorescent protein. Dev. Biol. 2000;228:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Touboul T., Hannan N.R., Corbineau S., Martinez A., Martinet C., Branchereau S., Mainot S., Strick-Marchand H., Pedersen R., Di Santo J. Generation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells under chemically defined conditions that recapitulate liver development. Hepatology. 2010;51:1754–1765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

