Fibrotic protein expression profiles in penile tissue of patients with erectile dysfunction
- PMID: 24075003
- PMCID: PMC4011715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.06.042
Fibrotic protein expression profiles in penile tissue of patients with erectile dysfunction
Abstract
Objective: To characterize transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1) and related signaling pathway proteins in a large cohort of human penile tissue (HPT) samples.
Methods: HPT was collected from patients undergoing penile prosthesis implantation for erectile dysfunction (ED) and divided into the following 2 groups: postradical prostatectomy ED (RP-ED; n = 57) and organic ED (O-ED; n = 30). HPT from patients undergoing partial penectomy without ED was used as controls (CON; n = 6). Western blot analysis was performed to investigate the protein expressions of TGFβ1, thrombospondin 1 (TSP1; an activator of TGFβ1), fibronectin (an extracellular matrix glycoprotein induced by TGFβ1), and a family of transcriptional factors activated by TGFβ1 (Smad2, phospho-Smad2-serine-465/467 [pSmad2], Smad3, phospho-Smad3-serine-423/425 [pSmad3]).
Results: Expressions of TGFβ1 and TSP1 were significantly higher in RP-ED (P <.05) and O-ED (P <.05) groups compared with that of the CON group and were not different between either ED groups. Expressions of Smad2, pSmad2, Smad3, pSmad3, and fibronectin were similar among all groups. Within the RP-ED group, a subgroup analysis showed that time from RP to penile prosthesis implantation was related to increased expression of pSmad2 (P <.05), and previous history of intracavernosal injection was related to increased expression of TGFβ1 (P <.05).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that TSP1- and TGFβ1-dependent fibrotic changes occur in penile tissue in patients with ED regardless of etiology. The unchanged expression of the Smad transcriptional factors may be reconciled by a Smad-independent downstream signaling pathway transmitting TGFβ1 signals.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
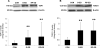
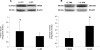
References
-
- Benson CR, Serefoglu EC, Hellstrom WJG. Sexual dysfunction following radical prostatectomy. J Androl. 2012;33:1143–1154. - PubMed
-
- Iacono F, Giannella R, Somma P, et al. Histological alterations in cavernous tissue after radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2005;173:1673–1676. - PubMed
-
- Border W, Noble N. Transforming Growth Factor Beta in Tissue Fibrosis. NEJM. 1994;331:1286–1291. - PubMed
-
- Jin HR, Chung YG, Kim WJ, et al. A mouse model of cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction: functional and morphological characterization of the corpus cavernosum. J Sex Med. 2010;7:3351–3364. - PubMed
-
- Nehra A, Gettman MT, Nugent M, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF- beta1) is sufficient to induce fibrosis of rabbit corpus cavernosum in vivo. J Urol. 1999;162:910–915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

