In vitro activity of natural honey alone and in combination with curcuma starch against Rhodotorula mucilaginosa in correlation with bioactive compounds and diastase activity
- PMID: 24075348
- PMCID: PMC3761142
- DOI: 10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60161-6
In vitro activity of natural honey alone and in combination with curcuma starch against Rhodotorula mucilaginosa in correlation with bioactive compounds and diastase activity
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the in vitro activity and synergism of the combinations of natural honey and curcuma starch against Rhodotorula mucilaginosa in correlation with total phenolic, flavonoid contents, and diastase activity.
Methods: The Folin-Ciocalteu test was used to determine the total polyphenols content and the flavonoid content was analyzed using by the aluminum chloride method. The antifungal activity of the natural honey, determined by an agar well diffusion assay and agar incorporation method.
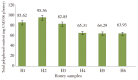
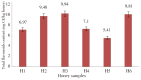
Results: Total phenolic content varied from (63.930.11) to (95.366.08) mg GAE/100 g honey as gallic acid equivalent. Total flavonoids content varied from (5.41±0.04) to (9.94±0.54) mg CE/100 g. Diastase activity values were between (7.3±2.8) and (26±2.8). The zone inhibition diameter for the six honey samples without starch ranged between 6 and 20 mm. When starch was mixed with honey and then added to well, a zone inhibition increase diameter 7 and 21 mm. The percentage increase was noticed with each variety and it ranged between 5% and 62.5%. The minimal inhibitory concentrations for the six varieties of honey without starch against Rhodotorula mucilaginosa ranged between 28% and 36% (v/v). When starch was incubated with honey and then added to media, a minimal inhibitory concentration drop has been noticed with each variety. It ranged between 6.66 % and 20% (w/v). No significant correlation was established between diastase activity and bioactive compounds.
Conclusions: The mixture of curcuma starch and honey could lead to the development of new combination antibiotics against Rhodotorula infections.
Keywords: Bioactive Compounds; Curcuma starch; Diastase number; Honey; Rhodotorula mucilaginosa.
Copyright © 2013 Asian Pacific Tropical Biomedical Magazine. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chen SC, Playford EG, Sorrell TC. Antifungal therapy in invasive fungal infections. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010;10(5):522–530. - PubMed
-
- Monk BC, Goffeau A. Outwitting multidrug resistance to antifungals. Science. 2008;321(5887):367–369. - PubMed
-
- Singla RK, Jaiswal N, Varadaraj BG, Jagani H. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Cocos nucifera Linn. (Arecaceae) endocarp extracts. Indo Global J Pharm Sci. 2011;1(4):354–361.
-
- Feás X, Estevinho ML. A Survey of the in vitro antifungal activity of heather (Erica Sp.) organic honey. J Med Food. 2011;14(10):1284–1288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources