Risk factors for prolonged length of stay after the stage 2 procedure in the single-ventricle reconstruction trial
- PMID: 24075564
- PMCID: PMC3964142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.07.063
Risk factors for prolonged length of stay after the stage 2 procedure in the single-ventricle reconstruction trial
Abstract
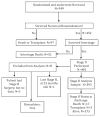
Background: The single-ventricle reconstruction trial randomized patients with single right ventricle lesions to a modified Blalock-Taussig or right ventricle-to-pulmonary artery shunt at the Norwood. This analysis describes outcomes at the stage 2 procedure and factors associated with a longer hospital length of stay (LOS).
Methods: We examined the association of shunt type with stage 2 hospital outcomes. Cox regression and bootstrapping were used to evaluate risk factors for longer LOS. We also examined characteristics associated with in-hospital death.
Results: There were 393 subjects in the analytic cohort. Median stage 2 procedure hospital LOS (8 days; interquartile range [IQR], 6-14 days), hospital mortality (4.3%), transplantation (0.8%), median ventilator time (2 days; IQR, 1-3 days), median intensive care unit LOS (4 days; IQR, 3-7 days), number of additional cardiac procedures or complications, and serious adverse events did not differ by shunt type. Longer LOS was associated (R(2) = 0.26) with center, longer post-Norwood LOS (hazard ratio [HR], 1.93 per log day; P < .001), nonelective timing of the stage 2 procedure (HR, 1.78; P < .001), and pulmonary artery (PA) stenosis (HR, 1.56; P < .001). By univariate analysis, nonelective stage 2 (65% vs 32%; P = .009), moderate or greater atrioventricular valve (AVV) regurgitation (75% vs 24%; P < .001), and AVV repair (53% vs 9%; P < .001) were among the risk factors associated with in-hospital death.
Conclusions: Norwood LOS, PA stenoses, and nonelective stage 2 procedure, but not shunt type, are independently associated with longer LOS. Nonelective stage 2 procedure, moderate or greater AVV regurgitation, and need for AVV repair are among the risk factors for death.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00115934.
Copyright © 2014 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pridjian AK, Mendelsohn AM, Lupinetti FM, Beekman RH, Dick M, Serwer G, et al. Usefulness of the bidirectional Glenn procedure as staged reconstruction for the functional single ventricle. Am J Cardiol. 1993;71:959–62. - PubMed
-
- Forbess JM, Cook N, Serraf A, Burke RP, Mayer JE, Jonas RA. An institutional experience with second- and third-stage palliative procedures for hypoplastic left heart syndrome: the impact of the bidirectional cavopulmonary shunt. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997;29:665–70. - PubMed
-
- Reddy VM, McElhinney DB, Moore P, Haas GS, Hanley FL. Outcomes after bidirectional cavopulmonary shunt in infants less than 6 months old. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997;29:1365–70. - PubMed
-
- Douglas WI, Goldberg CS, Mosca RS, Law IH, Bove EL. Hemi-Fontan procedure for hypoplastic left heart syndrome: outcome and suitability for Fontan. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;68:1361–7. - PubMed
-
- Kogon BE, Plattner C, Leong T, Simsic J, Kirshbom PM, Kanter KR. The bidirectional Glenn operation: a risk factor analysis for morbidity and mortality. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;136:1237–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109781/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109777/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL109737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL109781/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL085057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL085057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109778/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical