Anti-tau antibodies that block tau aggregate seeding in vitro markedly decrease pathology and improve cognition in vivo
- PMID: 24075978
- PMCID: PMC3924573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.046
Anti-tau antibodies that block tau aggregate seeding in vitro markedly decrease pathology and improve cognition in vivo
Abstract
Tau aggregation occurs in neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease and many other disorders collectively termed tauopathies. trans-cellular propagation of tau pathology, mediated by extracellular tau aggregates, may underlie pathogenesis of these conditions. P301S tau transgenic mice express mutant human tau protein and develop progressive tau pathology. Using a cell-based biosensor assay, we screened anti-tau monoclonal antibodies for their ability to block seeding activity present in P301S brain lysates. We infused three effective antibodies or controls into the lateral ventricle of P301S mice for 3 months. The antibodies markedly reduced hyperphosphorylated, aggregated, and insoluble tau. They also blocked development of tau seeding activity detected in brain lysates using the biosensor assay, reduced microglial activation, and improved cognitive deficits. These data imply a central role for extracellular tau aggregates in the development of pathology. They also suggest that immunotherapy specifically designed to block trans-cellular aggregate propagation will be a productive treatment strategy.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

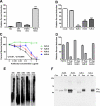





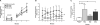
Comment in
-
Anti-tau antibodies: hitting the target.Neuron. 2013 Oct 16;80(2):254-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.009. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 24139027
-
Neurodegenerative disease: Tau immunotherapy targets transcellular propagation.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Dec;12(12):904. doi: 10.1038/nrd4179. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 24232374 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andoh T, Kuraishi Y. Direct action of immunoglobulin G on primary sensory neurons through Fc gamma receptor I. FASEB J. 2004;18:182–184. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte ET, Hyman BT. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992;42:631–639. - PubMed
-
- Bancher C, Braak H, Fischer P, Jellinger KA. Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer lesions and intellectual status in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease patients. Neurosci Lett. 1993;162:179–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
