Control of T helper 2 responses by transcription factor IRF4-dependent dendritic cells
- PMID: 24076050
- PMCID: PMC4110745
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.028
Control of T helper 2 responses by transcription factor IRF4-dependent dendritic cells
Abstract
CD4⁺ T cell differentiation is regulated by specialized antigen-presenting cells. Dendritic cells (DCs) produce cytokines that promote naive CD4⁺ T cell differentiation into T helper 1 (Th1), Th17, and inducible T regulatory (iTreg) cells. However, the initiation of Th2 cell responses remains poorly understood, although it is likely that more than one mechanism might be involved. Here we have defined a specific DC subset that is involved in Th2 cell differentiation in vivo in response to a protease allergen, as well as infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. We have demonstrated that this subset is controlled by the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), which is required for their differentiation and Th2 cell-inducing function. IRF4 is known to control Th2 cell differentiation and Th2 cell-associated suppressing function in Treg cells. Our finding suggests that IRF4 also plays a role in DCs where it controls the initiation of Th2 cell responses.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
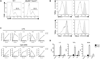
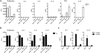
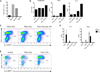
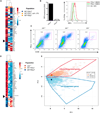
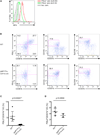
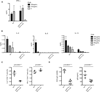
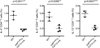
Comment in
-
T cell responses: a dendritic cell designed for two.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Dec;13(12):844-5. doi: 10.1038/nri3560. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24136622 No abstract available.
References
-
- Borkowski TA, Nelson AJ, Farr AG, Udey MC. Expression of gp40, the murine homologue of human epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM), by murine dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996;26:110–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

