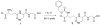Synthesis of azide derivative and discovery of glyoxalase pathway inhibitor against pathogenic bacteria
- PMID: 24076169
- PMCID: PMC3833347
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.09.011
Synthesis of azide derivative and discovery of glyoxalase pathway inhibitor against pathogenic bacteria
Abstract
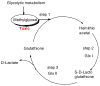
A glyoxalase inhibitor was synthesized and tested against Staphylococcus aureus for first time and showed MIC90 of 20 μg/ml. Henceforth, we synthesized unnatural azide derivative of the same inhibitor to improve the biological activity. In that order, an azide carboxylate was synthesized from dimethyl tartrate by tosylation and azide substitution. The synthesized, azide compound was coupled with glutathione derivative in high yield and tested against S. aureus and showed improved MIC90 of 5 μg/ml. In general, it can be also easily converted to unnatural β-amino acid in good yield. The shown methodology will be extended to study induced suicide in Burkholderia mallei, Francisella tularensis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis in future.
Keywords: Glutathione derivative; Glyoxalase pathway; Inhibitor; Metabolism; Staphylococcus aureus.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Organization, W. H. WHO. 2009.
-
- Stokvis E, Clugston SL, Honek JF, Heck AJ. J Protein Chem. 2000;19:389–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases