Effects of the neurotensin NTS₁ receptor agonist PD149163 on visual signal detection in rats
- PMID: 24076181
- PMCID: PMC3861869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.035
Effects of the neurotensin NTS₁ receptor agonist PD149163 on visual signal detection in rats
Abstract
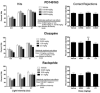
Antipsychotic drugs provide limited efficacy for cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Recent studies have found that the neurotensin NTS1 receptor agonist and putative atypical antipsychotic drug PD149163 reverses deficits in sensory-gating and novel object recognition, suggesting that this compound may have the potential to improve cognitive functioning in schizophrenia. The present study sought to extend these investigations by evaluating the effects of PD149163 on sustained attention using a visual signal detection operant task in rats. PD149163, the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine, and the dopamine D2/3 receptor antagonist raclopride all significantly decreased percent "hit" accuracy, while none of these compounds altered "correct rejections" (compared to vehicle control). Clozapine and raclopride significantly increased response latency, while high doses of PD149163 and raclopride significantly increased trial omissions. Nicotine, which was tested as a positive control, significantly improved overall performance in this task and did not affect response latency or trial omissions. The present findings suggest that neurotensin NTS1 receptor agonists, like antipsychotic drugs, may inhibit sustained attention in this task despite having different pharmacological mechanisms of action.
Keywords: Antipsychotic; Attention; NTS(1) receptor; Neurotensin; PD149163; Visual signal detection.
© 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: There are no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
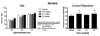
Similar articles
-
The discriminative stimulus effects of the neurotensin NTS1 receptor agonist PD149163 in rats: stimulus generalization testing with dopamine D1 and D2 receptor ligands.Drug Dev Res. 2014 Mar;75(2):47-58. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21171. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Drug Dev Res. 2014. PMID: 24668440
-
Repeated effects of the neurotensin receptor agonist PD149163 in three animal tests of antipsychotic activity: assessing for tolerance and cross-tolerance to clozapine.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Jan;128:78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2014.11.015. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 25433325 Free PMC article.
-
The quetiapine active metabolite N-desalkylquetiapine and the neurotensin NTS₁ receptor agonist PD149163 exhibit antidepressant-like effects on operant responding in male rats.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014 Dec;22(6):548-56. doi: 10.1037/a0038156. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25285844
-
Neurotensin agonists: possible drugs for treatment of psychostimulant abuse.Life Sci. 2003 Jun 27;73(6):679-90. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00388-6. Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 12801589 Review.
-
Novel treatments of schizophrenia: targeting the neurotensin system.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Apr;5(2):205-18. doi: 10.2174/187152706776359655. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16611093 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of acute and sustained pain manipulations on performance in a visual-signal detection task of attention in rats.Drug Dev Res. 2015 Jun;76(4):194-203. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21255. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Drug Dev Res. 2015. PMID: 26077965 Free PMC article.
-
Selective activation of Dopamine D3 receptors and norepinephrine transporter blockade enhances sustained attention.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Apr;148:178-188. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.01.003. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30633928 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive role of neurotensin receptor 1 in rats with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.Korean J Pain. 2020 Oct 1;33(4):318-325. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.4.318. Korean J Pain. 2020. PMID: 32989196 Free PMC article.
-
Task- and Treatment Length-Dependent Effects of Vortioxetine on Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction and Hippocampal Extracellular Acetylcholine in Rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Sep;358(3):472-82. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.233924. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 27402279 Free PMC article.
-
Vortioxetine Differentially Modulates MK-801-Induced Changes in Visual Signal Detection Task Performance and Locomotor Activity.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 13;9:1024. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01024. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30271344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnt J, Skarsfeldt T. Do novel antipsychotics have similar pharmacological characteristics? A review of the evidence. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1998;18:63–101. - PubMed
-
- Azmi N, Norman C, Spicer CH, Bennett GW. Effects of a neurotensin analogue (PD149163) and antagonist (SR142948A) on the scopolamine-induced deficits in a novel object discrimination task. Behav Pharmacol. 2006;17:357–362. - PubMed
-
- Binder EB, Kinkead B, Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB. Neurotensin and dopamine interactions. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:453–486. - PubMed
-
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E. Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;260:576–580. - PubMed
-
- Boules M, Warrington L, Fauq A, McCormick D, Richelson E. A novel neurotensin analog blocks cocaine- and D-amphetamine-induced hyperactivity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;426:73–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

