TRAIL on trial: preclinical advances in cancer therapy
- PMID: 24076237
- PMCID: PMC3880796
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.08.007
TRAIL on trial: preclinical advances in cancer therapy
Abstract
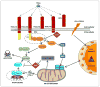
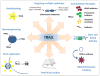
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, or TRAIL, is a promising anticancer agent as it can induce apoptosis in a wide range of cancers whilst generally sparing non-malignant cells. However, the translation of TRAIL into the clinic has been confounded by its short half-life, inadequate delivery methods, and TRAIL-resistant cancer cell populations. In this review, we discuss how TRAIL has been functionalized to diversify its traditional tumor-killing role and novel strategies to facilitate its effective deployment in preclinical cancer models. The successes and failures of the most recent clinical trials using TRAIL agonists are highlighted and we provide a perspective for improving its clinical implementation.
Keywords: TRAIL; apoptosis; cancer; stem cells; targeted therapy.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, et al. Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: the potential of recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL) Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:3621–3630. - PubMed
-
- Wiley SR, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Pitti RM, et al. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1996;271:12687–12690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

