Usp16: key controller of stem cells in Down syndrome
- PMID: 24076652
- PMCID: PMC3817468
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.220
Usp16: key controller of stem cells in Down syndrome
Abstract
Nature 501: 380–384
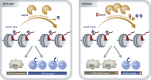
Somatic stem cell activity is critical for tissue homeostasis. Defects in stem cells are thought to be involved in many diseases, including inherited disorders and aging (He et al, 2009). In a recent paper published in Nature, Adorno et al (2013) demonstrate that there is a general somatic stem cell defect in Down syndrome (DS), a congenital disorder with triplication of human chromosome 21 (HSA21; Roper and Reeves, 2006; Mégarbané et al, 2009). They report that the deubiquitinase Usp16 gene located on HSA21 is a key epigenetic switch that regulates stem cell self-renewal and senescence in DS, and suggest that inhibiting or reducing HSA21 may be beneficial in treating the sequelae of DS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment on
-
Usp16 contributes to somatic stem-cell defects in Down's syndrome.Nature. 2013 Sep 19;501(7467):380-4. doi: 10.1038/nature12530. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24025767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmeliet G, David G, Cassiman JJ (1991) Cellular ageing of Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome cells in culture. Mut Res 256: 221–231 - PubMed
-
- He S, Nakada D, Morrison SJ (2009) Mechanisms of stem cell self-renewal. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25: 377–406 - PubMed
-
- Jacobs JJ, Kieboom K, Marino S, DePinho RA, van Lohuizen M (1999) The oncogene and Polycomb-group gene bmi-1 regulates cell proliferation and senescence through the ink4a locus. Nature 397: 164–168 - PubMed
-
- Joo HY, Zhai L, Yang C, Nie S, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Chang C, Wang H (2007) Regulation of cell cycle progression and gene expression by H2A deubiquitination. Nature 449: 1068–1072 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases