Programmable chemical controllers made from DNA
- PMID: 24077029
- PMCID: PMC4150546
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2013.189
Programmable chemical controllers made from DNA
Abstract
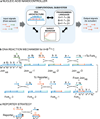
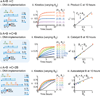
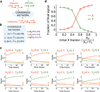
Biological organisms use complex molecular networks to navigate their environment and regulate their internal state. The development of synthetic systems with similar capabilities could lead to applications such as smart therapeutics or fabrication methods based on self-organization. To achieve this, molecular control circuits need to be engineered to perform integrated sensing, computation and actuation. Here we report a DNA-based technology for implementing the computational core of such controllers. We use the formalism of chemical reaction networks as a 'programming language' and our DNA architecture can, in principle, implement any behaviour that can be mathematically expressed as such. Unlike logic circuits, our formulation naturally allows complex signal processing of intrinsically analogue biological and chemical inputs. Controller components can be derived from biologically synthesized (plasmid) DNA, which reduces errors associated with chemically synthesized DNA. We implement several building-block reaction types and then combine them into a network that realizes, at the molecular level, an algorithm used in distributed control systems for achieving consensus between multiple agents.
Figures


Comment in
-
DNA computing: Molecules reach consensus.Nat Nanotechnol. 2013 Oct;8(10):703-5. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.202. Nat Nanotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24091452 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A programming language for composable DNA circuits.J R Soc Interface. 2009 Aug 6;6 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S419-36. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2009.0072.focus. Epub 2009 Jun 17. J R Soc Interface. 2009. PMID: 19535415 Free PMC article.
-
Neural network computation with DNA strand displacement cascades.Nature. 2011 Jul 20;475(7356):368-72. doi: 10.1038/nature10262. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21776082
-
Synthetic mixed-signal computation in living cells.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 3;7:11658. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11658. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27255669 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic biology: insights into biological computation.Integr Biol (Camb). 2016 Apr 18;8(4):518-32. doi: 10.1039/c5ib00274e. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Integr Biol (Camb). 2016. PMID: 27074335 Review.
-
Molecular Computation for Molecular Classification.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023 Mar;7(3):e2200203. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202200203. Epub 2023 Jan 29. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36709492 Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-Inhibitor: a time-sensitive molecular circuit based on DNA strand displacement.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 4;48(19):10691-10701. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa835. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33045746 Free PMC article.
-
Operant conditioning of stochastic chemical reaction networks.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Nov 18;18(11):e1010676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010676. eCollection 2022 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36399506 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of thermodynamics for molecular systems, and the importance of molecular systems for thermodynamics.Nat Comput. 2018;17(1):3-29. doi: 10.1007/s11047-017-9646-x. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Nat Comput. 2018. PMID: 29576756 Free PMC article.
-
Programming discrete distributions with chemical reaction networks.Nat Comput. 2018;17(1):131-145. doi: 10.1007/s11047-017-9667-5. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Nat Comput. 2018. PMID: 29576758 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumatic computers for embedded control of microfluidics.Sci Adv. 2023 Jun 2;9(22):eadg0201. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg0201. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37267360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koo OM, Rubinstein I, Onyuksel H. Role of nanotechnology in targeted drug delivery and imaging: a concise review. Nanomedicine: NBM. 2005;1(3):193–212. - PubMed
-
- Hess H. Engineering applications of biomolecular motors. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011;13:429–450. - PubMed
-
- Zhang DY, Seelig G. Dynamic DNA nanotechnology using strand-displacement reactions. Nature Chem. 2011;3(2):103–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

