Phase I study of vismodegib in children with recurrent or refractory medulloblastoma: a pediatric brain tumor consortium study
- PMID: 24077351
- PMCID: PMC3856244
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1425
Phase I study of vismodegib in children with recurrent or refractory medulloblastoma: a pediatric brain tumor consortium study
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the safety, dose-limiting toxicities, and pharmacokinetics of the smoothened inhibitor vismodegib in children with refractory or relapsed medulloblastoma.
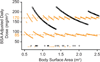
Experimental design: Initially, vismodegib was administered daily at 85 mg/m(2) and escalated to 170 mg/m(2). The study was then revised to investigate a flat-dosing schedule of 150 mg for patients with small body surface area (BSA, 0.67-1.32 m(2)) or 300 mg for those who were larger (BSA, 1.33-2.20 m(2)). Pharmacokinetics were performed during the first course of therapy, and the right knees of all patients were imaged to monitor bone toxicity. Immunohistochemical analysis was done to identify patients with Sonic Hedgehog (SHH)-subtype medulloblastoma.
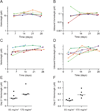
Results: Thirteen eligible patients were enrolled in the initial study: 6 received 85 mg/m(2) vismodegib, and 7 received 170 mg/m(2). Twenty eligible patients were enrolled in the flat-dosing part of the study: 10 at each dosage level. Three dose-limiting toxicities were observed, but no drug-related bone toxicity was documented. The median (range) vismodegib penetration in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was 0.53 (0.26-0.78), when expressed as a ratio of the concentration of vismodegib in the CSF to that of the unbound drug in plasma. Antitumor activity was seen in 1 of 3 patients with SHH-subtype disease whose tumors were evaluable, and in none of the patients in the other subgroups.
Conclusions: Vismodegib was well tolerated in children with recurrent or refractory medulloblastoma; only two dose-limiting toxicities were observed with flat dosing. The recommended phase II study dose is 150 or 300 mg, depending on the patient's BSA. Clin Cancer Res; 19(22); 6305-12. ©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, Sturla LM, Angelo M, McLaughlin ME, et al. Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature. 2002;415:436–442. - PubMed
-
- Thompson MC, Fuller C, Hogg TL, Dalton J, Finkelstein D, Lau CC, et al. Genomics identifies medulloblastoma subgroups that are enriched for specific genetic alterations. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1924–1931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

