ZNF804A and cortical structure in schizophrenia: in vivo and postmortem studies
- PMID: 24078172
- PMCID: PMC3984519
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbt123
ZNF804A and cortical structure in schizophrenia: in vivo and postmortem studies
Abstract
Recent evidence indicated that the ZNF804A (rs1344706) risk allele A is associated with better cognitive performance in patients with schizophrenia. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that ZNF804A may also be related to relatively intact gray matter volume in patients. To further explore these putatively protective effects, the impact of ZNF804A on cortical thickness and folding was examined in this study. To elucidate potential molecular mechanisms, an allelic-specific gene expression study was also carried out. Magnetic resonance imaging cortical thickness and folding were computed in 55 genotyped patients with schizophrenia and 40 healthy controls. Homozygous risk allele carriers (AA) were compared with AC/CC carriers. ZNF804A gene expression was analyzed in a prefrontal region using postmortem tissue from another cohort of 35 patients. In patients, AA carriers exhibited significantly thicker cortex in prefrontal and temporal regions and less disturbed superior temporal cortical folding, whereas the opposite effect was observed in controls, ie, AA carrier status was associated with thinner cortex and more severe altered cortical folding. Along with this, our expression analysis revealed that the risk allele is associated with lower prefrontal ZNF804A expression in patients, whereas the opposite effect in controls has been observed by prior analyses. In conclusion, our analyses provide convergent support for the hypothesis that the schizophrenia-associated ZNF804A variant mediates protective effects on cortex structure in patients. In particular, the allele-specific expression profile in patients might constitute a molecular mechanism for the observed protective influence of ZNF804A on cortical thickness and folding and potentially other intermediate phenotypes.
Keywords: ZNF804A; cortical folding; cortical thickness; gene expression; psychosis; rs1344706; schizophrenia; susceptibility gene.
Figures
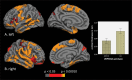
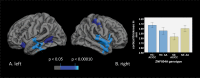
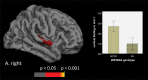
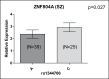
Comment in
-
ZNF804A protein is widely expressed in human brain neurons: possible implications on normal brain structure and pathomorphologic changes in schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2014 May;40(3):499-500. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbt237. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Schizophr Bull. 2014. PMID: 24442852 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- O’Donovan MC, Craddock N, Norton N, et al. Identification of loci associated with schizophrenia by genome-wide association and follow-up. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1053–1055 - PubMed
-
- Hill MJ, Jeffries AR, Dobson RJ, Price J, Bray NJ. Knockdown of the psychosis susceptibility gene ZNF804A alters expression of genes involved in cell adhesion. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:1018–1024 - PubMed
-
- Esslinger C, Walter H, Kirsch P, et al. Neural mechanisms of a genome-wide supported psychosis variant. Science. 2009;324:605. - PubMed
-
- Esslinger C, Kirsch P, Haddad L, et al. Cognitive state and connectivity effects of the genome-wide significant psychosis variant in ZNF804A. Neuroimage. 2011;54:2514–2523 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

