Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in breast cancer—a newly defined prognostic marker
- PMID: 24078229
- PMCID: PMC10358065
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-013-0160-z
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in breast cancer—a newly defined prognostic marker
Abstract
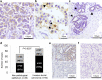
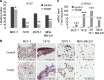
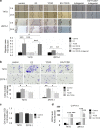
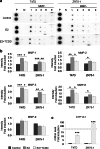
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) has been reported to exert various anticancer effects upon breast carcinoma cells in vitro but its details have remained largely unknown. Therefore, we first examined the AhR status in 90 invasive ductal carcinoma patients using immunohistochemistry. We then performed in vitro studies including wound healing assay, invasion assay, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) protein array in order to further elucidate the roles of AhR signaling in breast carcinoma. The status of AhR immunoreactivity was inversely correlated with histological grade (P = 0.0135) and Ki-67 labeling index (LI; P = 0.0087) of the patients. In addition, results of both uni- and multivariate analyses revealed that AhR in carcinoma cells turned out an independent prognostic factor with a protective relative risk (P = 0.0179). An administration of 10 nM 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a ligand of AhR, significantly decreased Ki-67 LI in an AhR-dependent fashion in MCF-7, T47D, ZR75-1, and MDA-MB-231. Wound healing and invasion assays performed in T47D and ZR75-1 further demonstrated that 10 nM TCDD inhibited estrogen-induced migration and invasion of cells. MMP proteins associated with AhR in breast carcinoma cells were also firstly identified. These results demonstrated that AhR in breast carcinoma cells is considered a newly defined histological prognostic parameter of the breast cancer patients and effects of AhR activation on proliferation and MMPs expression may be related to the relatively good clinical outcome of AhR-positive breast cancer patients.
Figures

References
-
- Bertazzi PA, Zocchetti C, Guercilena S, Consonni D, Tironi A, Landi MT, Pesatori AC. Dioxin exposure and cancer risk: a 15-year mortality study after the “Seveso accident”. Epidemiology. 1997;8(6):646–652. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

