Synthesis of a novel thiazolidinedione and evaluation of its modulatory effect on IFN- γ , IL-6, IL-17A, and IL-22 production in PBMCs from rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 24078927
- PMCID: PMC3773918
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/926060
Synthesis of a novel thiazolidinedione and evaluation of its modulatory effect on IFN- γ , IL-6, IL-17A, and IL-22 production in PBMCs from rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease frequently characterized by chronic synovitis of multiple joints. The pathogenesis of RA is complex and involves many proinflammatory cytokines as Th17 related ones. PPAR γ is a nuclear receptor activator that represses proinflammatory gene expression. Thus, this work aimed to synthetize a new thiazolidinedione (TZD) analogue based on a well-known anti-inflammatory and PPAR γ agonist activity of this ring and evaluate its anti-inflammatory activity. After chemical structure confirmation, the compound named 5-(5-bromo-2-methoxy-benzylidene)-3-(2-nitro-benzyl)-thiazolidine-2,4-dione TM17 was submitted to cytokine releasing inhibition and PPAR γ genetic modulation assays. The new compound showed no toxicity on human and murine cells, decreasing IL-6 secretion by murine splenocytes and reducing IL-17A, IL-22, and IFN- γ expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with RA. TM17 was more efficient in modulating the mRNA expression of PPAR γ than its well-used TZD agonist rosiglitazone. Surprisingly, TM17 was efficient on IL-17A and IFN- γ reduction, like the positive control methylprednisolone, and presented a better effect on IL-22 levels. In conclusion, PBMCs obtained from RA patients under TM17 treatment present a significant reduction in IL-17A, IL-22, and IFN- γ levels, but not IL-6 when compared with nontreated cells, as well as increase PPAR γ mRNA expression in absence of stimulus addressing it as a promising molecule in RA treatment.
Figures


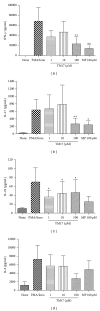
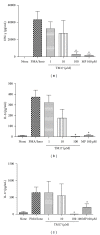

References
-
- Wolfe F, Mitchell DM, Sibley JT, et al. The mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 1994;37(4):481–494. - PubMed
-
- Brasington DR., Jr. Clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Hochberg MC, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH, editors. Rheumatology. 5th edition. Vol. 1. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 829–837.
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2011;365(23):2205–2219. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2007;7(6):429–442. - PubMed
-
- Chabaud M, Fossiez F, Taupin J, Miossec P. Enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1-induced IL-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes and its regulation by Th2 cytokines. Journal of Immunology. 1998;161(1):409–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

