Bidirectional regulation of P body formation mediated by eIF4F complex formation in sensory neurons
- PMID: 24080374
- PMCID: PMC3951963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.09.048
Bidirectional regulation of P body formation mediated by eIF4F complex formation in sensory neurons
Abstract
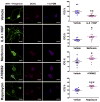
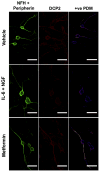
Processing (P) bodies are RNA granules that comprise key cellular sites for the metabolism of mRNAs. In certain cells, including neurons, these RNA granules may also play an important role in storage of mRNAs in a translationally dormant state. Utilizing nerve growth factor (NGF) and interleukin 6 (IL6), which stimulate cap-dependent translation in sensory neurons, and adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators, which inhibit cap-dependent translation, we have tested the hypothesis that cap-dependent translation is linked to P body formation in mammalian sensory neurons. Treatment with NGF and IL6 decreases, whereas metformin increases biochemical association of the P body marker and translational repressor/decapping activator Rck/p54/dhh1 with the 5'-mRNA-cap suggesting an ordered assembly of P bodies. Likewise, diverse AMPK activators enhance P body formation while NGF and IL6 decrease P bodies in sensory neurons. This bidirectional P body plasticity readily occurs in the axonal compartment of these neurons. These studies indicate that P body formation is intricately linked to cap-dependent translation in mammalian sensory neurons suggesting an important role for these organelles in the regulation of mRNA metabolism in the adult PNS.
Keywords: AMPK; P bodies; Translation initiation; Trigeminal ganglion; eIF4F; mRNA degradation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Emerging evidence for P body function in the peripheral nervous system.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Mar 20;563:166-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.10.059. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24211685 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barbee SA, Estes PS, Cziko AM, Hillebrand J, Luedeman RA, Coller JM, Johnson N, Howlett IC, Geng C, Ueda R, Brand AH, Newbury SF, Wilhelm JE, Levine RB, Nakamura A, Parker R, Ramaswami M. Staufen- and FMRP-containing neuronal RNPs are structurally and functionally related to somatic P bodies. Neuron. 2006;52:997–1009. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

