APOE associated hemispheric asymmetry of entorhinal cortical thickness in aging and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24080518
- PMCID: PMC3851589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2013.09.006
APOE associated hemispheric asymmetry of entorhinal cortical thickness in aging and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Across species structural and functional hemispheric asymmetry is a fundamental feature of the brain. Environmental and genetic factors determine this asymmetry during brain development and modulate its interaction with brain disorders. The e4 allele of the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE-4) is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, associated with regionally specific effects on brain morphology and function during the life span. Furthermore, entorhinal and hippocampal hemispheric asymmetry could be modified by pathology during Alzheimer's disease development. Using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging and a cortical unfolding technique we investigated whether carrying the APOE-4 allele influences hemispheric asymmetry in the entorhinal cortex and the hippocampus among patients with Alzheimer's disease as well as in middle-aged and older cognitively healthy individuals. APOE-4 carriers showed a thinner entorhinal cortex in the left hemisphere when compared with the right hemisphere across all participants. Non-carriers of the allele showed this asymmetry only in the patient group. Cortical thickness in the hippocampus did not vary between hemispheres among APOE-4 allele carriers and non-carriers. The APOE-4 allele modulates hemispheric asymmetry in entorhinal cortical thickness. Among Alzheimer's disease patients, this asymmetry might be less dependent on the APOE genotype and a more general marker of incipient disease pathology.
Keywords: APOE-4 allele; Cortical unfolding; Entorhinal cortex; Hippocampus; Magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
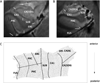
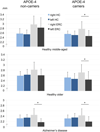
References
-
- Amaral DG, Insausti R. Hippocampal formation. In: Praxinos G, editor. The Human Nervous System. San Diego: Academic Press; 1990. pp. 711–755.
-
- Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Flory J, Damasio AR, Van Hoesen GW. The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Cerebral Cortex. 1991;1:103–116. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J, Scahill RI, Schott JM, Frost C, Rossor MN, Fox NC. Does Alzheimer's disease affect hippocampal asymmetry? Evidence from a cross-sectional and longitudinal volumetric MRI study. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. 2005;19:338–344. - PubMed
-
- Benbow CP, Stanley JC. Sex differences in mathematical reasoning ability: more facts. Science. 1983;222:1029–1031. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin R, Leake A, McArthur FK, Ince PG, Candy JM, Edwardson JA, Morris CM, Bjertness E. Protective effect of apoE epsilon 2 in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1994;344:473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 DA034728/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AG13308/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AG025831/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010123/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013308/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH052453/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50-AG16570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH-AG58156/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH-52453/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG025831/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

